In this vocabulary lesson, we will learn the names of animals in English. I have included flashcards and many pictures to help you memorise them easily. Next time, when you see them, you will know what to call them.
1. Names of animals in English and their subclasses
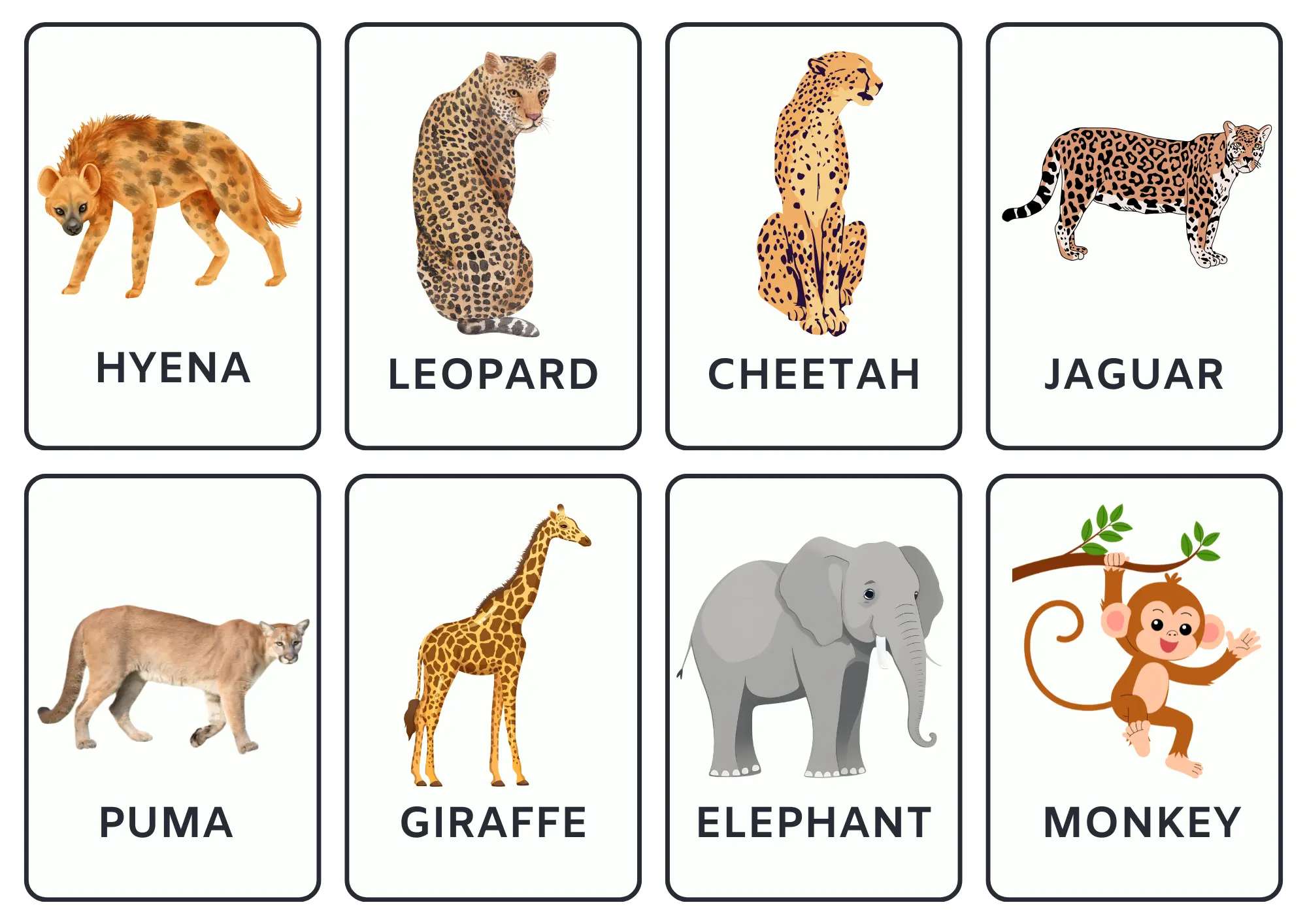
1.1 Wild animals
Wild animals are non-domestic animals that live in their natural habitats such as forests, jungles, savannas, and mountains. They help maintain ecological balance.
Below is a comprehensive list of names of wild animals in English.

Lion 
Elephant 
Giraffe

Otter 
Mouse 
Squirrel
Predators, like tigers and wolves, hunt and kill other animals for food. They help control the populations of herbivores, preventing overgrazing and preserving vegetation.
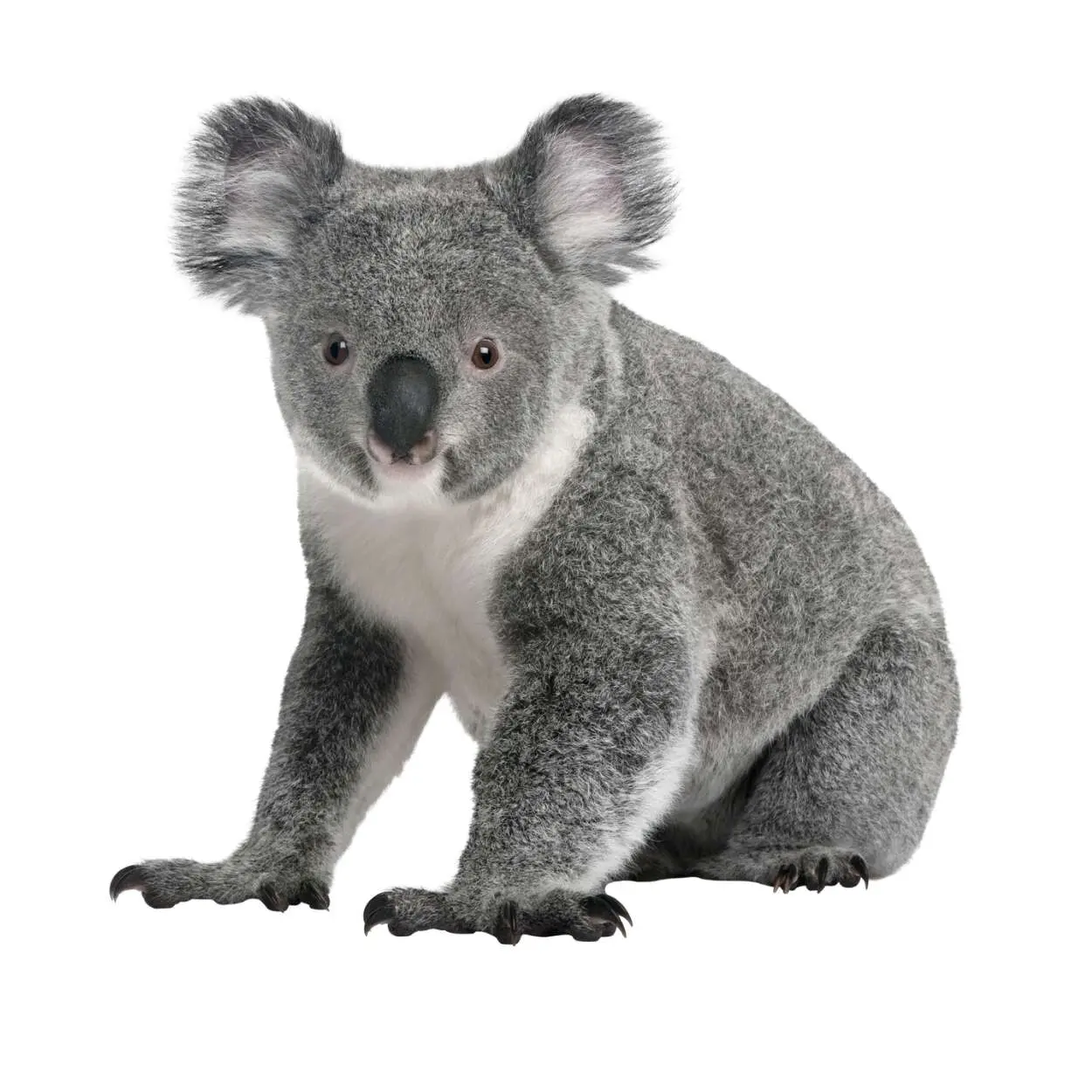

Koala 
Kangaroo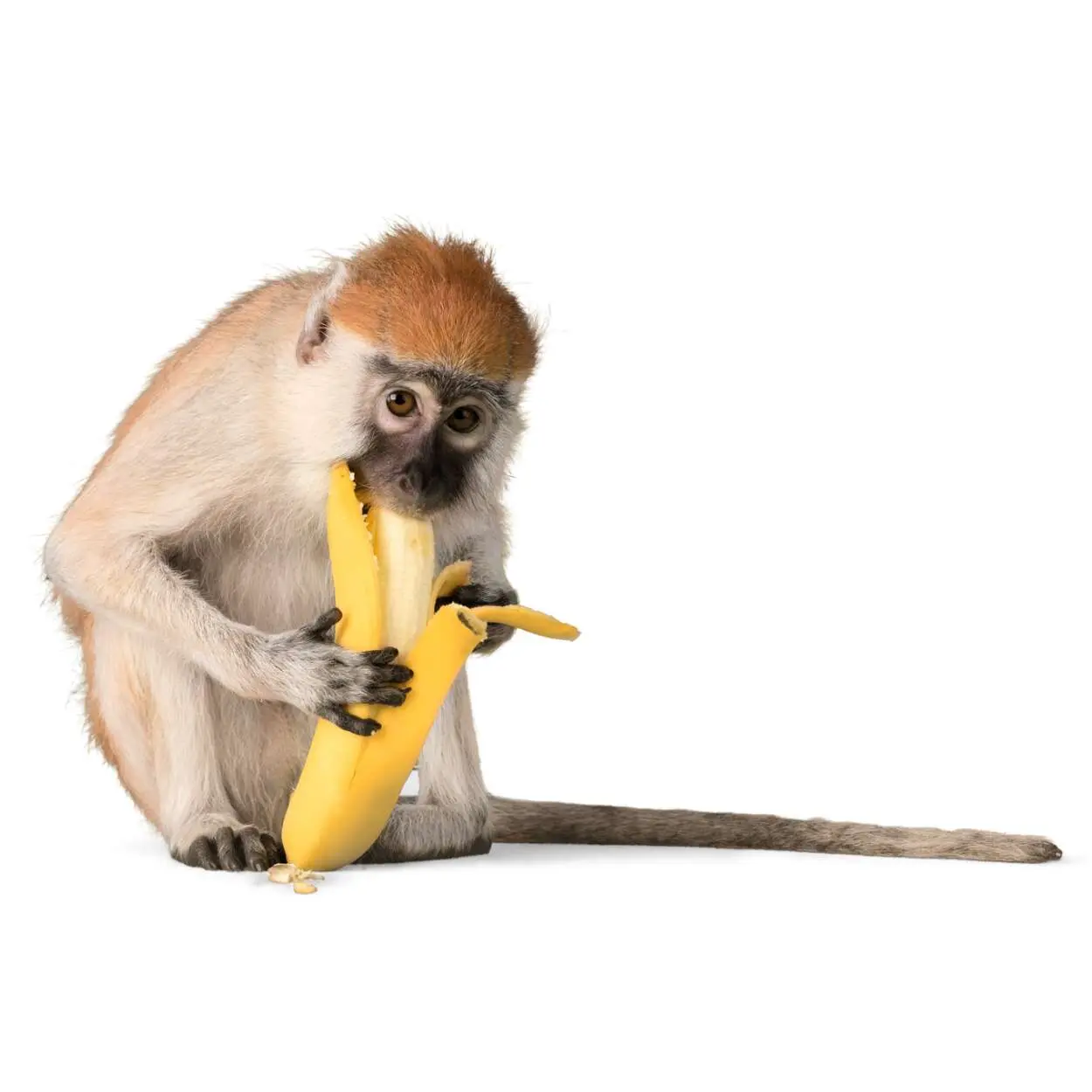 
Monkey
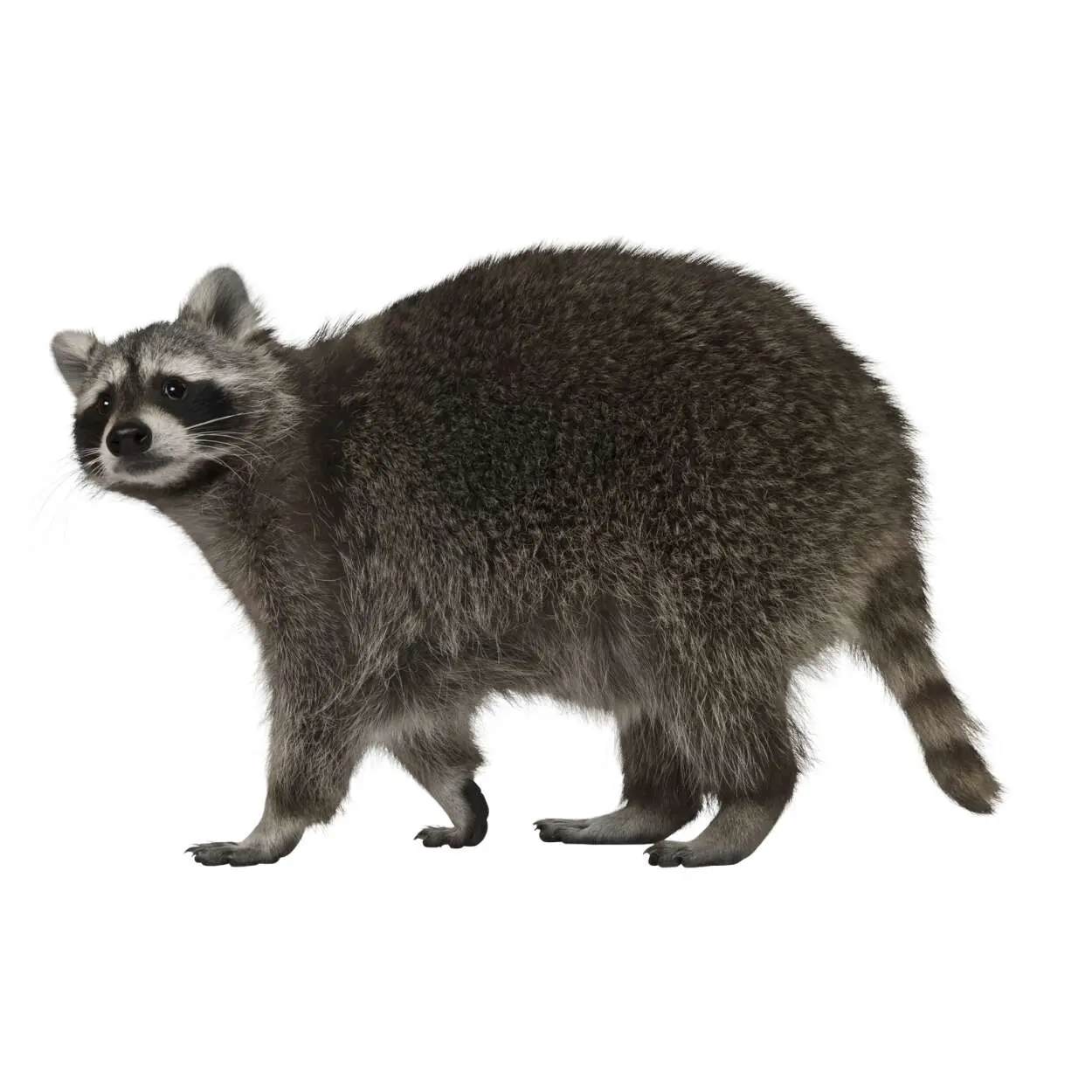

Raccoon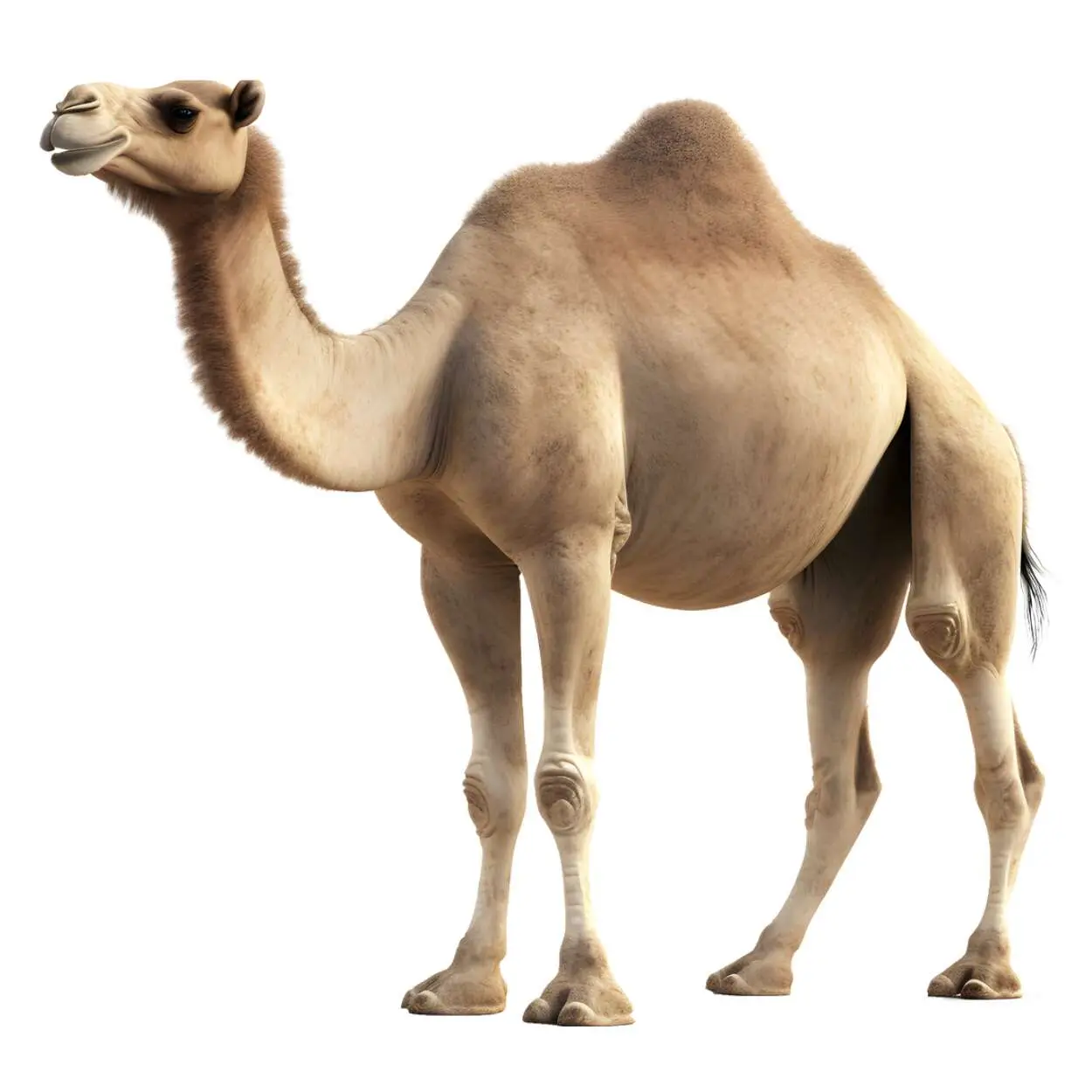 
Camel 
Zebra
Scavengers eat animals that they did not kill. Hyenas and vultures are scavengers. They help reduce the spread of disease.

Wolf 
Hippopotamus 
Tiger

Leopard 
Meerkat 
Hyena
Herbivores, like deer and zebras, contribute to plant diversity by feeding on various flora, enabling new growth.

Panda 
Bear 
Polar bear

Penguin 
Gorilla 
Fox

Bat
1.2 Insects
Insects are the most numerous and diverse group of animals on Earth. They inhabit nearly every environment, from icy mountains to scorching deserts. They outnumber humans by 1.4 billion to one.
Below, you’ll find the names of insects across various species and types.

Ant 
Bee 
Butterfly

Ladybug 
Mosquito 
Moth
The combined weight of insects vastly surpasses that of humanity. They make up 90% of animal species.

Fly 
Cockroach 
Flea

Silverfish 
Dragonfly 
Spider
Insects have existed for over 350 million years. They have been on eath before dinosaurs and flowering plants. Coleoptera (beetles) are the largest known order of insects, followed by Lepidoptera (butterflies and moths), Diptera (true flies), and Hymenoptera, the group that includes ants, bees, and wasps.

Caterpillar 
Grasshopper 
Beetle

Termite
Small animals, like insects and rodents, also help the ecosystems by dispersing seeds and creating habitats that support biodiversity.
1.3 Pets
Pets are animals that we keep at home companionship, amusement, or emotional support rather than for work or economic purposes.
Dogs, cats, birds, fish, and small mammals like rabbits or hamsters are examples of pets.
The list below contain common names of pet animals.

Cat 
Dog 
Pigeon
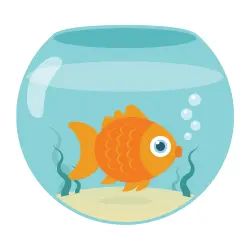
Goldfish 
Betta fish 
Rottweiler
A goldfish is a freshwater fish that people keep as a pet in aquariums. It originally comes from China and belongs to the carp family. Goldfish eat plants, small insects and prepared fish food. They can live for more than ten years if well cared for.

Coton de Tulear 
Cockatiel 
Lovebird

Hedgehog 
Chinchilla 
Ferret
The Coton de Tulear is a small dog breed from Madagascar. It is named after a city located in the southwest of Madagascar. It gets along well with children and other pets. It weighs around 4 to 6 kg.

Canary 
Parakeet 
Gerbil

Guinea pig 
Hamster 
Shih Tzu
The Shih Tzu originated from Tibet. It has short snout, large bright eyes, and curled tail. It weighs between 4 kg and 7.5 kg and is 20 to 28 cm tall.

Bulldog 
Poodle 
Chihuahua

Dachshund 
Pug 
Cocker Spaniel
Bulldogs have a life expectancy between 8 and 10 years. Although they look tough, they are friendly. Do you like dogs? What kind of dogs do you have?

Border Collie 
Siberian Husky 
Dalmatian

Basset Hound 
Great Dane 
Doberman Pinscher
What dog breed do you think is the most intelligent? Well, the Border Collie is widely considered the smartest dog breed. They learn very fast. They can understand complex commands.

Saint Bernard 
Greyhound 
Maltese

Yorkshire Terrier 
Australian Shepherd 
Pembroke Welsh Corgi
The Saint Bernard is named after Saint Bernard of Menthon, a 10th-century monk who founded a hospice on the Great St Bernard Pass in the Alps.

German Shepherd 
Alaskan Malamute 
Cavalier King Charles Spaniel

Jack Russell Terrier 
Boston Terrier 
Samoyed
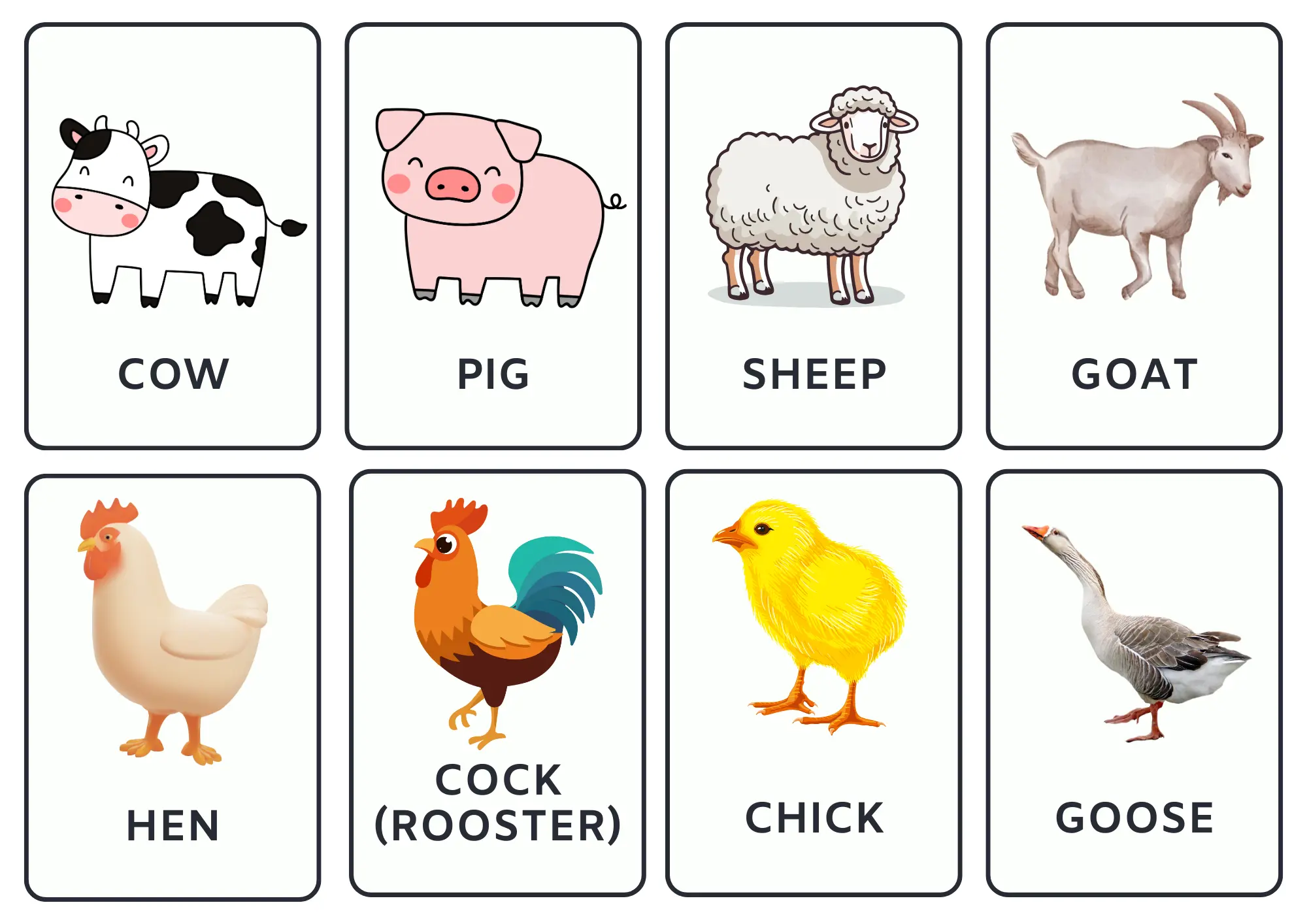
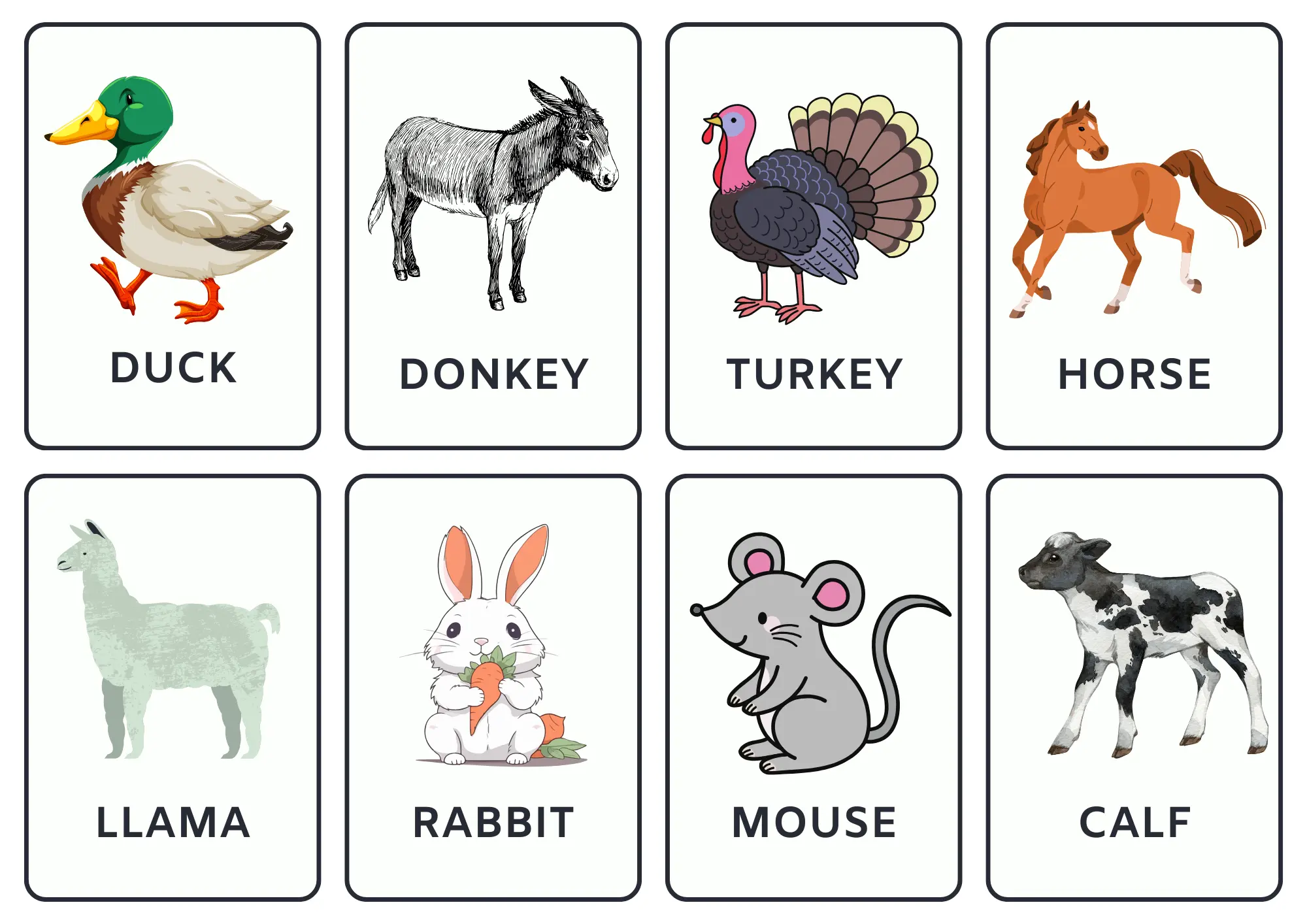
1.4 Livestock
Farm animals are raised primarily for agricultural purposes, such as producing food, clothing, labour, or other resources.
In the list below, you will learn the names of farm animals in English.
Horse 
Cow 
Cock

Hen 
Chick 
Goose
Farm animals live on farms. Farmers take care of them to produce food and do farm work. For example, in many developing countries, farmers use cows to plough the soil.

Gosling 
Duck 
Duckling

Rabbit 
Sheep 
Pig
Farm animals sustain rural economies and provide food such as meat, milk, and eggs. I grew up in a village where most people depend on farming to live.

Calf 
Bull 
Bison

Turkey 
Deer 
Goat

Donkey
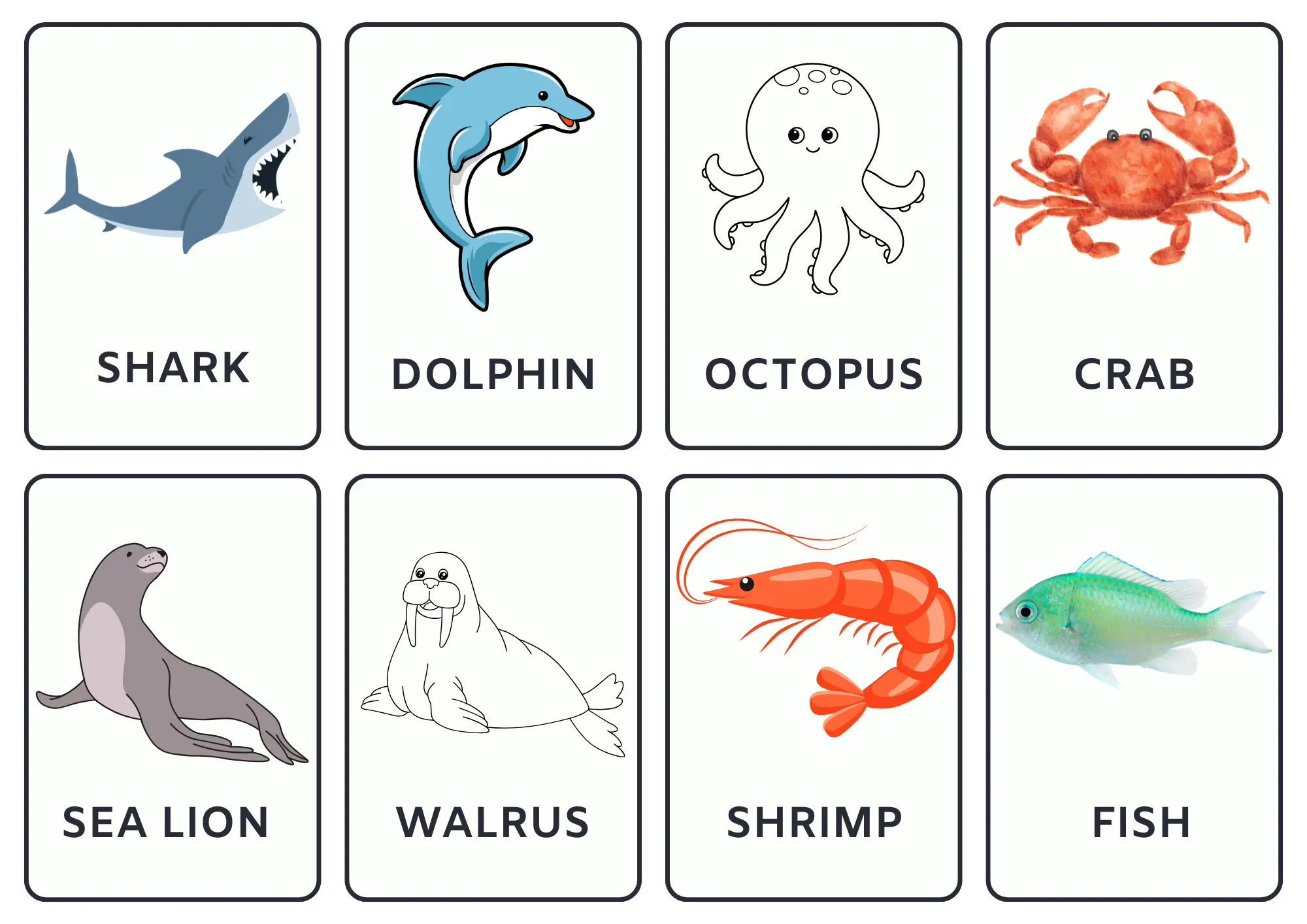
1.5 Names of marine animals
Marine animals live in the sea. They come in different types, such as cephalopods, crustaceans, shellfish, corals, invertebrates, fish, mammals, seabirds, sharks, rays, and turtles.
The list below contains the names of marine animals in English.

Fish 
Shark 
Dolphin

Whale 
Octopus 
Sea turtle
Cephalopods, such as octopuses and squids, are intelligent molluscs with tentacles. Crustaceans, like crabs and shrimp, have hard shells and segmented bodies.

Jellyfish 
Stingray 
Seahorse

Squid 
Lobster 
Crab
Shellfish, including clams and oysters, are also popular seafood. Corals are invertebrates that form reefs, while other invertebrates include jellyfish and starfish.

Shrimp 
Starfish 
Sea urchin

Eel 
Clownfish 
Swordfish
Fish breathe using gills and come in three main types: bony, cartilaginous, and jawless. Marine mammals, like whales and seals, are warm-blooded and nurse their young.

Tuna 
Barracuda 
Manta ray

Blue tang 
Angelfish 
Oyster
Seabirds feed from the ocean and nest on land. Sharks and rays have flexible skeletons made of cartilage, while turtles are cold-blooded reptiles that lay their eggs on beaches.

Mussel 
Sea anemone 
Seal

Walrus 
Sea lion 
Manatee
1.6 Birds
Birds have feathers, wings, and beaks. They lay eggs, and most of them can fly. They are found in different places, such as in the forests, deserts, and even in cities.
They help spread seeds and control insect populations. Here is a list of bird names in English.

Owl 
Toucan 
Vulture

Macaw 
Parrot 
Crow
Birds eat different kinds of food, including seeds, insects, and small animals. They communicate with each other using songs and calls.

Peacock 
Dove 
Stork

Eagle
1.7 Reptiles
Reptiles have backbones. They usually have dry skin covered in scales. They lay eggs, and many live on land, although some can be found in water.
The list below contains different names of reptiles in English.

Snake 
Alligator 
Crocodile

Komodo dragon 
Chameleon 
Gecko
Unlike mammals, reptiles do not have fur or hair. They need warm temperatures to stay active.

Turtle 
Horned lizard 
Iguana

Cobra 
Python 
Boa constrictor
Some snakes are venomous. They use their venom to catch prey and protect themselves. Cobras, vipers, and mambas are examples of venemous snakes. Be careful when you come across them.

Black mamba 
Rattlesnake
We should protect wild animals because extinction is permanent. When species are gone, we can't bring them back.

2. Endangered species
Endangered species are animals and plants that are at risk of extinction due to various factors, including habitat loss, climate change, poaching, and pollution.
We need to protect these species to maintain biodiversity and the health of the ecosystems. Here’s an overview of different categories of endangered species:
2.1. Critically endangered animals
Critically endangered species face an extremely high risk of extinction in the wild.
- Sumatran orangutan: Habitat destruction due to logging and palm oil plantations has severely impacted their populations.
- Vaquita: This small porpoise, found in the Gulf of California, is on the brink of extinction, with estimates suggesting fewer than 30 individuals remain due to illegal fishing practices.
- Javan rhino: With only around 80 individuals left, the Javan rhino is confined to a single national park in Indonesia, making it susceptible to disease and habitat loss.
2.2. Vulnerable species
Vulnerable species are not currently facing an immediate threat of extinction but are at risk if the factors contributing to their decline are not addressed. These animals typically have declining populations and may experience habitat loss or hunting pressures.
- African elephant: While still numerous, African elephants face threats from poaching for ivory and habitat loss due to human expansion.
- Polar bear: As climate change impacts their sea ice habitat, polar bears are becoming increasingly vulnerable, relying on diminishing ice to hunt seals.
- Bengal tiger: With habitat destruction and poaching for their fur, the Bengal tiger is classified as vulnerable, although conservation efforts are underway to protect their habitats.
2.3. Extinct animals
Extinct animals are those that no longer exist, primarily due to human activities. Understanding extinct species can help highlight the importance of conservation efforts for currently endangered species.
- Woolly mammoth: Once roamed the Earth during the Ice Age, woolly mammoths went extinct due to a combination of climate change and overhunting by early humans.
- Dodo: The dodo, a flightless bird native to Mauritius, was driven to extinction in the 17th century by hunting and the introduction of non-native species.
- Passenger pigeon: Once abundant in North America, the passenger pigeon became extinct in the early 20th century due to intense hunting and habitat destruction.
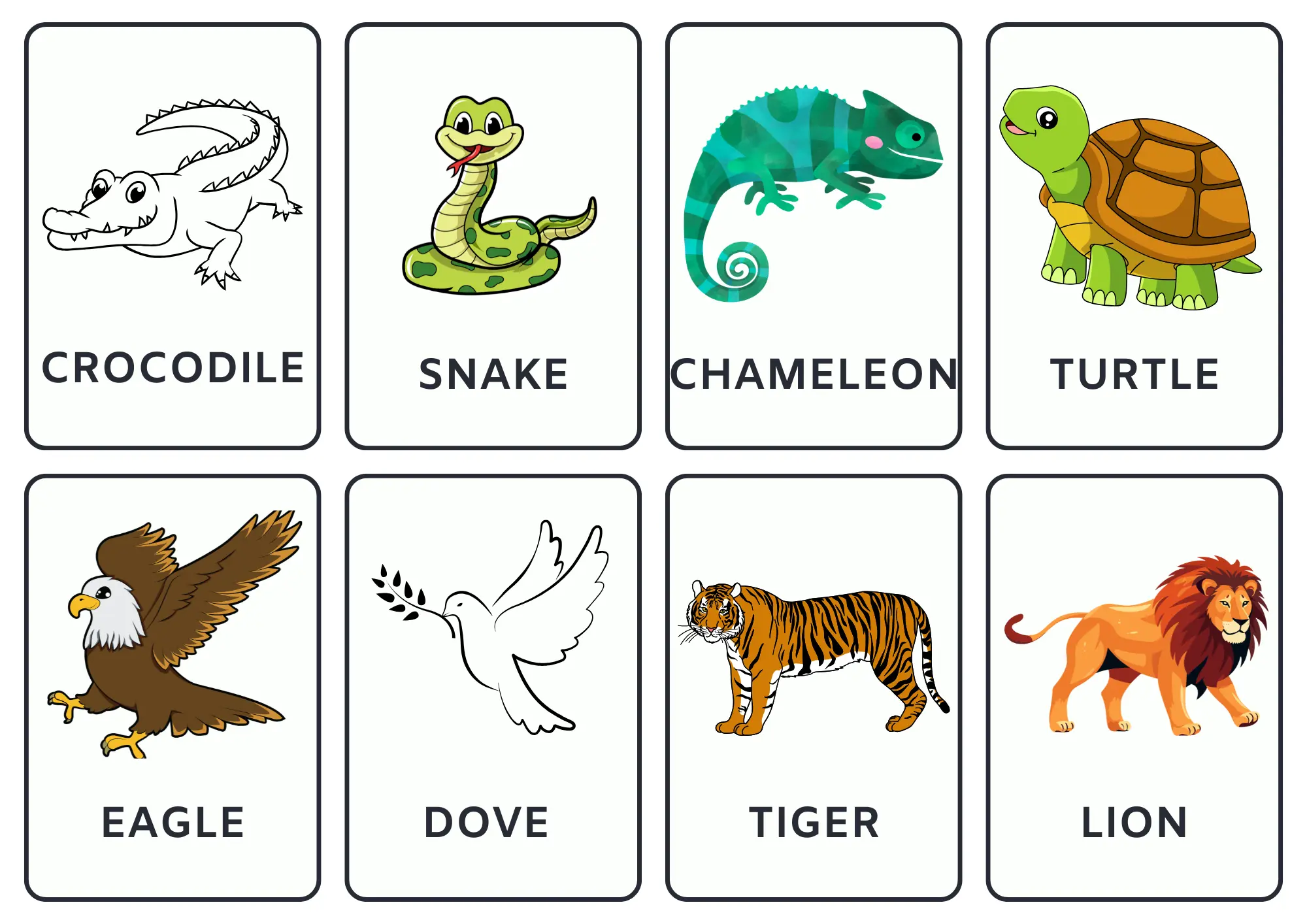
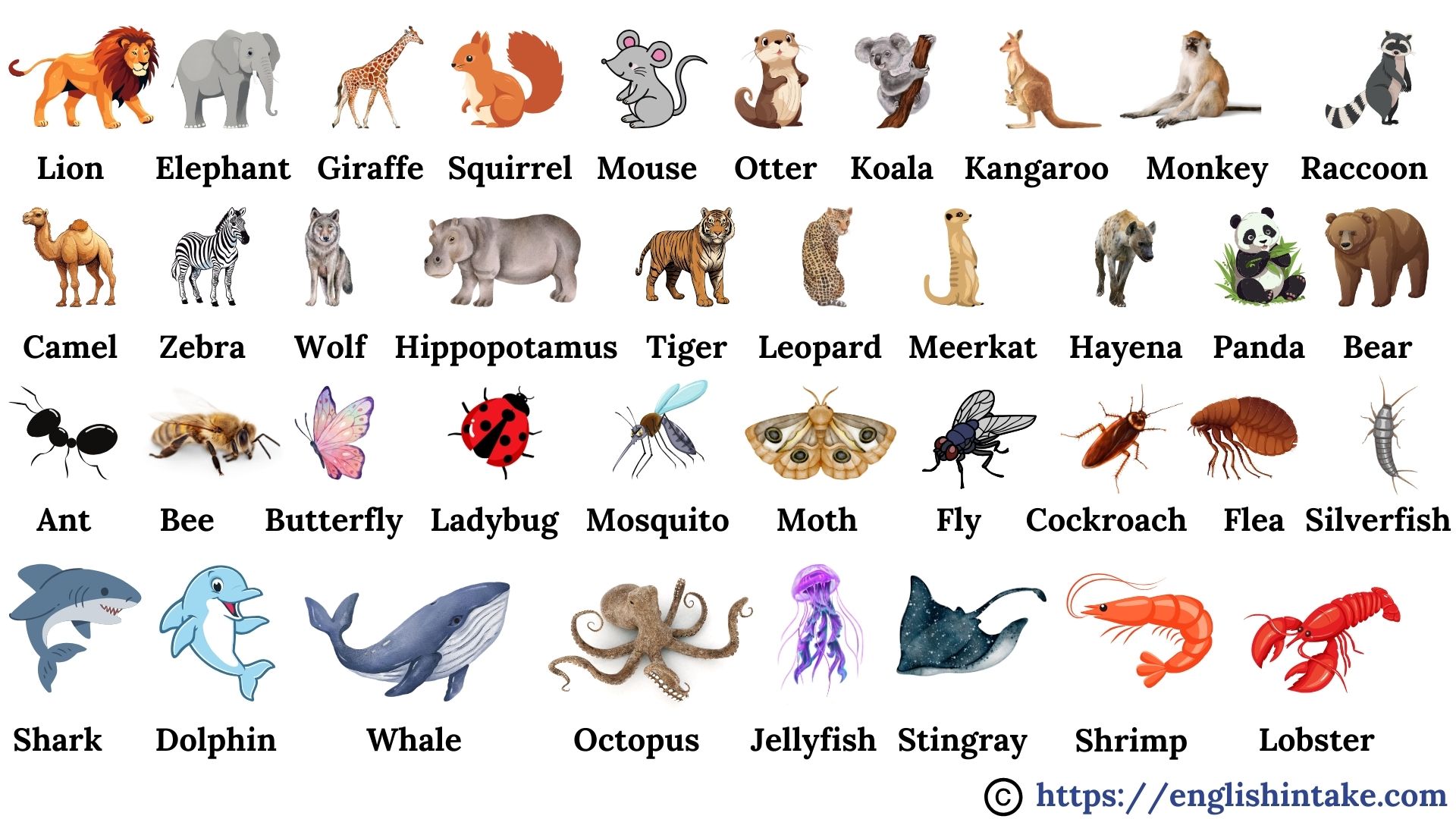
3. Animals flashcards
These flashcards contain the names of various animals. Click the arrow buttons to slide through the carousels.