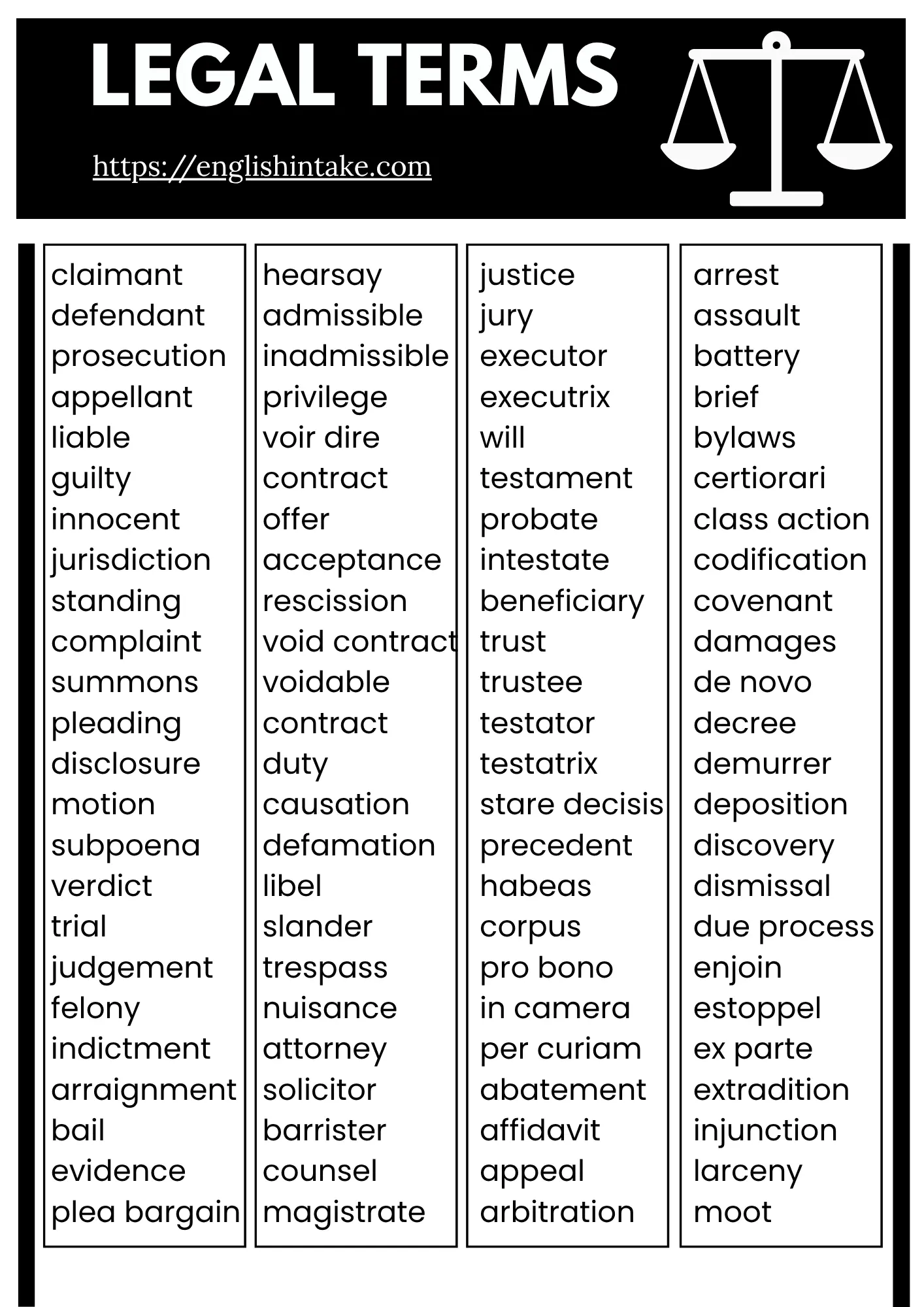
1. Common legal terms in alphabetical order
This glossary of legal terms contains over 100 words with definitions to help you get familiar with complex jargon used in court proceedings.
To cancel or repeal a law or agreement.
AccessorySomeone who helps another person commit a crime, either before or after the crime.
AcquittalA judgment that a person is not guilty of the crime they were accused of.
Ad hocFor a specific purpose or situation; temporary.
AdjournmentThe postponement of a court hearing or session to a later date.
AffidavitA written statement made under oath, to be used as evidence in court.
AlibiA claim or piece of evidence that someone was elsewhere when a crime was committed, used to show they could not have committed it.
AllegationA claim or assertion that someone has done something illegal or wrong, typically without proof.
Amicus curiae"Friend of the court." An impartial advisor, often a non-profit organization, who offers information or opinions to the court on a matter of law.
AppealA request to a higher court to review a decision made by a lower court.
AppellantThe party who appeals a court decision to a higher court.
AppelleeThe party against whom an appeal is made.
ArbitrationA method of resolving disputes outside of court, where a neutral third party (the arbitrator) hears both sides and makes a binding decision.
ArraignmentA court hearing where a person accused of a crime is informed of the charges and asked to enter a plea (guilty, not guilty, or no contest).
ArrestTo take a person into custody because there is probable cause to believe they committed a crime.
AssaultAn intentional act that causes another person to reasonably apprehend immediate harmful or offensive contact. (Often confused with battery, which is the actual contact).
AsylumProtection granted by a nation to someone who has left their native country as a political refugee.
Money or property given to the court to ensure that an arrested person will appear for their trial.
BailiffA court officer responsible for maintaining order in the courtroom and taking care of the jury.
BankruptcyA legal process for individuals or businesses who cannot pay their debts, allowing them to eliminate or repay some or all of their debts under court supervision.
BatteryThe intentional harmful or offensive physical contact with another person without their consent.
Bench warrantAn order issued by a judge for the arrest of a person who failed to appear in court as required.
BeneficiaryA person or entity who receives benefits from a will, trust, or life insurance policy.
Beyond a reasonable doubtThe standard of proof required in criminal cases, meaning the evidence presented is so convincing that there is no other logical explanation for the facts except that the defendant committed the crime.
BriefA written legal argument submitted to a court, outlining a party's legal and factual arguments.
Burden of proofThe obligation on one party in a legal case to prove a particular fact or set of facts.
Law established by the outcomes of previous court cases, as opposed to law created by legislation.
Certiorari (Writ of)An order from a higher court to a lower court to send up the record of a case for review. This is how the Supreme Court typically chooses which cases to hear.
ChargeA formal accusation that a person has committed a crime.
Civil lawThe branch of law dealing with disputes between individuals or organizations, rather than criminal offenses. Examples include contract disputes, property issues, and personal injury claims.
Class action lawsuitA lawsuit in which a large group of people with similar claims sue a common defendant.
CodicilAn addition or supplement that explains, modifies, or revokes a will or part of one.
Common lawA system of law based on custom and court decisions, rather than written laws. (Prevalent in countries like the UK, USA, Canada).
ComplaintThe initial document filed in a civil lawsuit, stating the plaintiff's claims against the defendant.
Concurrent sentencesPrison sentences for multiple crimes that are served at the same time.
Concurring opinionA judge's opinion that agrees with the majority decision in a case but for different reasons.
Contempt of courtDisobeying or disrespecting the authority of a court, which can result in a fine or imprisonment.
Contingency feeA fee arrangement in which a lawyer receives a percentage of the financial recovery only if the case is successful.
ContractA legally binding agreement between two or more parties.
ConvictionA formal declaration by a judge or jury that someone is guilty of a criminal offence.
CounterclaimA claim made by a defendant against a plaintiff in a lawsuit, in opposition to the plaintiff's own claim.
Cross-examinationThe questioning of a witness by the opposing attorney in a trial.
Money awarded by a court to a person who has suffered a loss or injury due to the wrongful act of another.
De factoExisting in fact, though not officially recognized by law.
De jureExisting by right or according to law.
Declaratory judgmentA court's official statement of the rights of parties to a lawsuit, without ordering any action or awarding damages.
DecreeAn official order or decision by a court.
Default JudgmentA judgment entered against a party who fails to appear in court or respond to a lawsuit.
DefendantThe person or entity against whom a lawsuit is filed or who is accused of a crime.
DemurrerA legal pleading that admits the facts as alleged by the opposing party but argues that those facts are not legally sufficient to support a claim or defence.
DepositionA sworn out-of-court testimony of a witness, recorded for use in court proceedings.
DiscoveryThe formal process in a lawsuit where parties exchange information and evidence relevant to the case before trial.
Dissenting opinionA judge's opinion that disagrees with the majority decision in a case.
Due ProcessThe legal requirement that the state must respect all legal rights owed to a person. It balances the power of law of the land and protects individual persons from it.
A legal right to use another person's land for a specific purpose (e.g., a right of way).
EmancipationThe legal process by which a minor is freed from the control of their parents or guardians and gains the legal rights of an adult.
Eminent DomainThe power of the government to take private property for public use, even if the owner does not want to sell, provided they receive just compensation.
EnjoinTo legally prohibit someone from doing something through a court order (an injunction).
EscrowA financial arrangement where a third party holds money or assets until specific conditions are met.
EstoppelA legal principle that prevents a person from asserting a fact or right that is contrary to an earlier position or statement.
EvictionThe legal process by which a landlord removes a tenant from a rental property.
EvidenceInformation presented in court to prove or disprove facts in a case.
Ex ParteA legal proceeding conducted for the benefit of only one party, without notice to or argument from the other party.
ExhibitA document or object presented as evidence in court.
ExtraditionThe official process by which a state or country transfers a suspected or convicted criminal to another state or country where they are wanted for trial or punishment.
A serious crime, typically punishable by imprisonment for more than a year or by death.
Fiduciary dutyA legal obligation of one party to act in the best interest of another party.
ForeclosureThe legal process by which a lender takes possession of a property when the borrower fails to make mortgage payments.
A legal procedure by which a creditor can collect money from a debtor by taking a portion of their wages or seizing funds from their bank account.
Grand juryA group of citizens convened to determine whether there is enough evidence to issue an indictment (formal accusation) in a criminal case.
Guardian ad litemA person appointed by the court to represent the interests of a minor or an incompetent person in a legal proceeding.
A legal order requiring a person under arrest to be brought before a judge or into court, especially to secure the person's release unless lawful grounds are shown for their detention.
HearsaySecond-hand information; a statement made out-of-court by someone other than the witness testifying, offered as evidence to prove the truth of the matter asserted. Generally not admissible in court.
In law, the process of calling into question the credibility of a witness. In politics, the process of formally charging a public official with misconduct.
IndictmentA formal accusation by a grand jury that there is enough evidence to bring criminal charges against a person.
InjunctionA court order requiring a person to do or stop doing a specific act.
In re"In the matter of." Used in case titles that do not involve opposing parties, such as a bankruptcy or probate proceeding.
InterrogatoriesWritten questions sent by one party to another in a lawsuit, which must be answered under oath.
IntestateDying without a valid will.
The bringing together of multiple parties or claims in a single lawsuit.
JudgmentThe final decision of a court in a legal case.
JurisdictionThe legal authority of a court to hear and decide a case.
JurisprudenceThe theory or philosophy of law.
JuryA group of citizens selected to hear evidence in a trial and decide the facts of the case.
A legal claim against property to secure payment of a debt.
LitigationThe process of taking legal action; a lawsuit.
Locus standiThe right or capacity to bring a case to court.
The performance of an act that is illegal or wrongful.
Mandamus (Writ of)A court order commanding a public official to perform an act that they are legally required to do.
Mens rea"Guilty mind." The mental state or intent required to commit a crime.
MisdemeanorA less serious crime than a felony, typically punishable by a fine or imprisonment for less than a year.
Mitigating circumstancesFactors that may lessen the severity of a crime or the punishment for it.
MotionA formal request made to a judge for an order or ruling.
Failure to exercise the care that a reasonably prudent person would exercise in a similar situation, resulting in harm to another.
Nolo contendere"No contest." A plea in a criminal case where the defendant does not admit guilt but also does not dispute the charges, leading to a conviction without a trial.
NoticeLegal communication informing a party of a legal action or event.
A solemn promise to tell the truth, typically sworn on a religious text or by affirming.
ObjectionA formal protest made in court to a question or statement, indicating that it is improper or illegal.
Opinion (court)A written statement by a judge or court explaining the decision in a case.
OrdinanceA law passed by a local government (e.g., a city or county).
A person trained in legal matters who performs legal tasks under the supervision of a lawyer.
PardonThe action of officially forgiving someone for a crime and removing any remaining punishment.
ParoleThe conditional release of a prisoner before the completion of their sentence, often subject to supervision.
PartiesThe individuals or entities involved in a lawsuit (e.g., plaintiff, defendant).
PerjuryThe crime of intentionally lying under oath in court.
PetitionA formal written request to a court or other official body.
PlaintiffThe person or entity who brings a lawsuit against another.
Plea BargainAn agreement between a prosecutor and a defendant where the defendant pleads guilty to a lesser charge or to fewer charges in exchange for a lighter sentence.
PleadingA formal statement, written or oral, made to a court presenting a party's arguments and claims.
Power of attorneyA legal document authorizing one person to act on behalf of another in legal or financial matters.
PrecedentA legal principle or rule established in an earlier court case that is considered authoritative for future similar cases.
Preliminary hearingA hearing in a criminal case to determine if there is enough evidence to proceed to trial.
Prima facie"On the face of it." Evidence that, unless rebutted, is sufficient to prove a fact or case.
Probable causeReasonable grounds for believing that a crime has been committed or that a person is involved in a crime. Required for arrests and searches.
ProbateThe legal process of proving a will to be valid and distributing a deceased person's estate.
Pro bonoLegal work performed free of charge for the public good.
ProsecutorThe lawyer who represents the government in criminal cases and tries to prove the defendant is guilty.
To cancel or make void (e.g., to quash an indictment or a subpoena).
The process by which a judge removes themselves from a case due to a conflict of interest or bias.
RemandTo send a case back to a lower court for further action.
RemedyThe means by which a right is enforced or a violation of a right is prevented or compensated for.
ReparationsPayments or other forms of compensation made to victims of a wrong or injustice.
Res judicata"A matter judged." A legal principle stating that a matter that has been decided by a court cannot be re-litigated between the same parties.
Restraining orderA court order that prohibits a person from doing a specific act, often used in cases of domestic violence or harassment.
RetainerAn upfront payment made by a client to a lawyer to secure their services.
ReversalThe decision of a higher court to overturn the judgment of a lower court.
Riparian rightsRights of landowners whose property borders a body of water, such as a river or lake.
A penalty or punishment imposed for breaking a law or rule.
Search warrantA legal document issued by a judge authorizing law enforcement to search a specific location for evidence of a crime.
SequestrationIn a trial, the isolation of a jury to prevent outside influence. The seizure of property by court order.
Service of processThe formal delivery of legal documents (like a summons or complaint) to a defendant or other party in a lawsuit.
SettlementAn agreement reached between parties in a lawsuit to resolve the dispute without going to trial.
SlanderSpoken defamation; making false and damaging statements about someone. (Contrast with libel, which is written).
Specific performanceA court order requiring a party to fulfill the terms of a contract, rather than paying damages.
Stare decisis"To stand by things decided." The legal principle that courts should follow precedents set in previous cases.
StatuteA written law passed by a legislative body.
Statute of limitationsA law that sets a maximum time after an event within which legal proceedings may be initiated.
SubpoenaA legal document ordering a person to appear in court or to produce documents.
SummonsA legal document notifying a defendant that a lawsuit has been filed against them and ordering them to appear in court or respond.
A formal written or spoken statement, especially one given in a court of law.
TortA civil wrong that causes a claimant to suffer loss or harm, resulting in legal liability for the person who commits the tortious act. Examples include negligence, assault, and defamation.
TranscriptA written record of spoken words, such as court proceedings.
TrustA legal arrangement where one party (the trustee) holds property for the benefit of another (the beneficiary).
When one person takes advantage of a position of power over another to persuade them to enter into a contract or make a will that is not in their best interest.
Unilateral contractA contract in which one party makes a promise in exchange for the other party's performance of an act.
UsuryThe illegal practice of lending money at excessively high interest rates.
The geographic location where a trial or legal action can be heard.
VerdictThe formal decision or finding made by a jury in a court case.
Voir dire"To speak the truth." The process of questioning prospective jurors to determine their suitability for jury service.
To intentionally give up a right or claim.
WarrantA legal document issued by a judge authorizing an arrest, search, or seizure of property.
WillA legal document that specifies how a person's assets are to be distributed after their death.
WitnessA person who sees an event or has knowledge about a case and provides testimony in court.
WritA formal written order issued by a court.
2. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What’s the difference between a felony and a misdemeanor?
A felony is a serious crime punishable by more than one year in prison (e.g., robbery, murder). A misdemeanor is a less serious offence, usually punishable by less than one year in jail or fines (e.g., petty theft, vandalism).
What does “beyond a reasonable doubt” mean?
It’s the standard of proof in criminal cases. The evidence must be so convincing that there is no reasonable doubt the accused committed the crime.
What is the role of a prosecutor?
A prosecutor is a lawyer who represents the government in criminal cases and tries to prove the defendant is guilty beyond a reasonable doubt.
How is a subpoena different from a summons?
A subpoena orders someone to appear in court or provide documents. A summons notifies someone they are being sued and must respond to the court.
What does “pro bono” mean in legal work?
“Pro bono” means legal work done voluntarily and free of charge, usually to help someone who cannot afford a lawyer.
What’s the difference between a plaintiff and a defendant?
The plaintiff is the person who files a lawsuit. The defendant is the person or party being sued or accused.
What is “due process”?
Due process is the legal right to fair procedures before being deprived of life, liberty, or property. It ensures laws are applied equally and fairly.
