Table of contents
1. What is the future continuous tense?
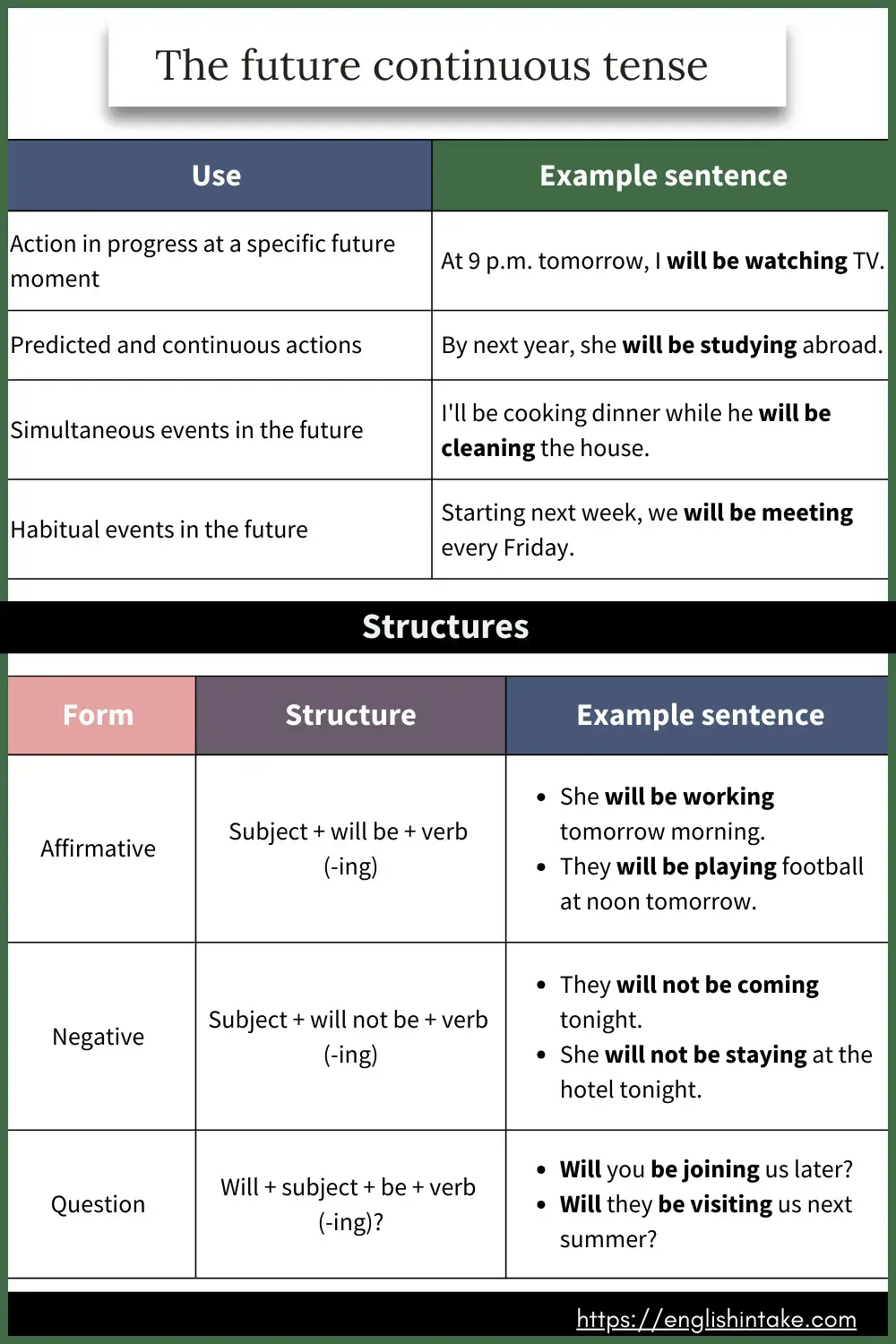
The future continuous tense describes an action that is predicted to take place at a particular point of time in the future and may progress beyond this time.
2. Examples
- What song will you be singing at my birthday party?
- At this time next month, I will be travelling to London.
- Don’t call me at 9 p.m. because I’ll be sleeping then.
- She will be dancing at 2 p.m. tomorrow.
3. Forms
3.1 Affirmative
Subject + will be + present participle (-ing form) + object
- I will be studying at the library tomorrow at 3 PM.
- They will be playing basketball in the park later.
The first example means that if someone goes to the library at precisely 3 PM tomorrow, they should expect to find you there studying. Similarly, the second sentence indicates that if you go to the park at some point in the future, you’ll see them already playing basketball.
3.2 Negative
Subject + will not (won’t) + be + present participle (-ing form) + object
- She will not be working tomorrow.
- He will not be taking a nap this afternoon.
3.3 Interrogative
Will + subject + be + present participle (-ing form) + object?
- Will you be watching the movie with us tonight?
- Will you be crying when I die?
3.4 Interrogative negative
Will + subject + not be + present participle (-ing form) + object?
- Will he not be going to the concert with us tonight?
- Will she not be studying for the exam tomorrow?
You will be staying
He will be staying
She will be staying
It will be staying
We will be staying
You will be staying
They will be staying
You’ll be staying
He’ll be staying
She’ll be staying
It’ll be staying
We’ll be staying
You’ll be staying
They’ll be staying
You will not be staying
He will not be staying
She will not be staying
It will not be staying
We will not be staying
You will not be staying
They will not be staying
You won’t be staying
He won’t be staying
She won’t be staying
It won’t be staying
We won’t be staying
You won’t be staying
They won’t be staying
Will you be staying?
Will he be staying?
Will she be staying?
Will it be staying?
Will we be staying?
Will you be staying?
Will they be staying?
Will you not be staying?
Will he not be staying?
Will she not be staying?
Will it not be staying?
Will we not be staying?
Will you not be staying?
Will they not be staying?
Won’t you be staying?
Won’t he be staying?
Won’t she be staying?
Won’t it be staying?
Won’t we be staying?
Won’t you be staying?
Won’t they be staying?
4. Use of the future continuous tense
4.1 Expressing predicted and continuous actions
The future continuous describes an action that is predicted to take place at a particular point of time in the future and may progress beyond this time. It is also used to describe events that are the result of previous arrangements or decisions.
- We will be using hand signals when we are ready.
- When the school bell rings, the students will be taking their final exams.
- I’ll be lounging by the pool and soaking up the sun this time next week.
- I’ll be meeting the new CEO tomorrow.
- Unfortunately, I won't be attending my best friend's wedding next month.
- In five years, the company will be launching its first satellite into space.
- Beyoncé will be performing her hit songs during the concert tonight.
- Will you be staying with us for the rest of the day?
4.2 Talking about simultaneous events in the future
The future continuous tense describes simultaneous events that are expected to happen in the future.
- The referee will be tracking my time and distance while I am running. ( Remember that we do not use the future tenses after time clauses such as when, as soon as, before, after, until, unless.)
- While I am singing, you will be playing the piano.
- I will be watering the plants, and you will be planting vegetables.
- We will be studying English while they are playing games.
- During your birthday party next week, we will be singing happy birthday to you while you are blowing out the candles on your cake.
- When the Dragon Endurance spacecraft reaches its orbit, the astronauts will be conducting experiments while the mission control team is monitoring their progress and ensuring their safety.
4.3 Expressing habitual events taking place in the future
The future continuous can also be used to describe future events that are part of a routine.
- We will be resuming our weekly seminars next week.
- Will you be leaving early tomorrow, as usual?
- Will you be taking the same train tomorrow?
- As usual, the Pope will be addressing the world on Christmas Day at midday.
- We will be doing the same exercises as yesterday.
- During this year's swearing-in ceremony, the new President will be reciting the same oath as his predecessors.
5. Future simple vs future continuous
The future continuous tense is mainly used to describe future actions that will progress beyond their starting point. However, the future simple tense is used to describe a short action. Let's study the following examples:
- I will sleep at 9 AM.
- I will be sleeping when you get back.
The first example describes the action of going to bed at 9 AM. This is a short action. The second example indicates that you will already be asleep when he/she returns, and you will continue to sleep for a certain period.
We use the future continuous tense instead of the future simple tense when we do not want to indicate willingness.
- Will you join us for dinner tonight? (You invite them to join you for dinner.)
- Will you be joining us for dinner tonight? (You ask about their plans.)
6. Summary