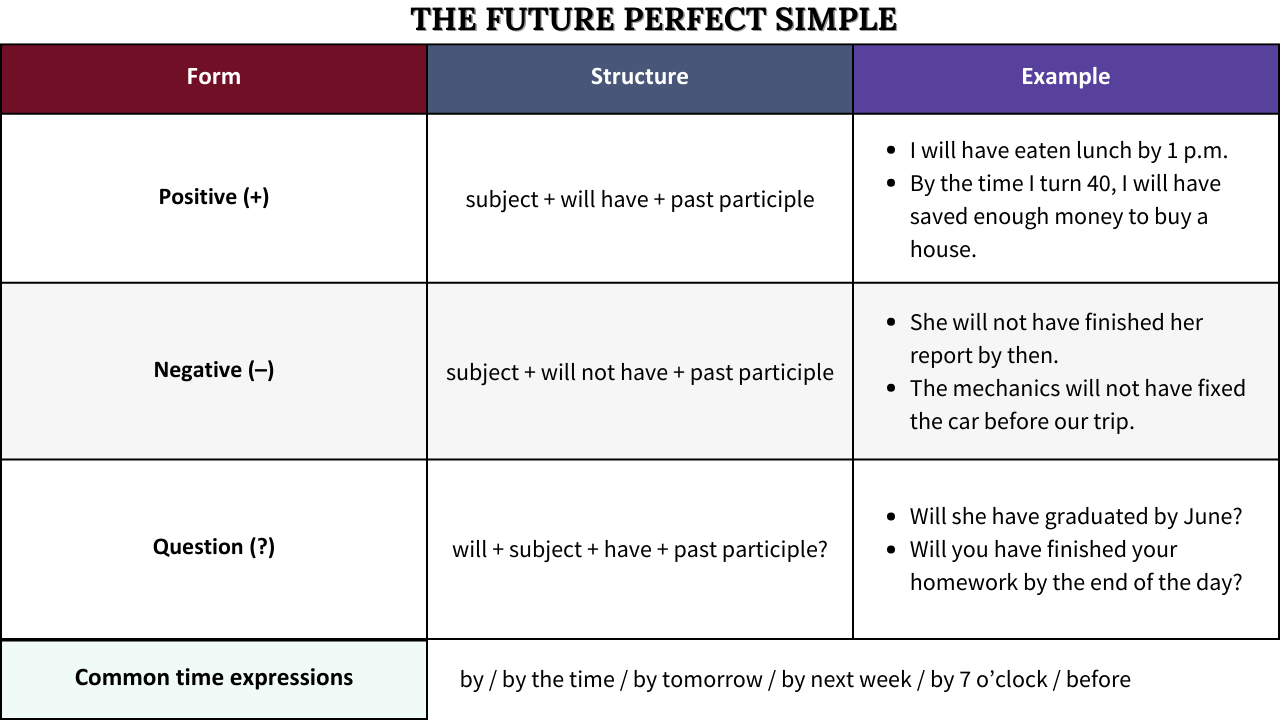
The future perfect tense expresses something you will finish in the future before something else happens. “By the time he comes home, I will have cleaned the house.” In this sentence, the action of cleaning the house will be completed before the man arrives. Let’s examine the structure and grammar rules in the next section.
1. Form of the future perfect tense
1.1 Affirmative
Subject + will + have + past participle + object
1. I will have left by 11 AM.
2. He will have read the entire book by next week.
3. We will have planted all the trees by noon.
4. By the end of the month, I will have written 30 blog posts.
5. The company will have expanded to ten cities by the end of next year.
6. The kids will have gone to bed by 9 PM.
7. The chef will have prepared the meal by the time the guests arrive.
8. The teacher will have graded all the exam papers by Friday.
1.2 Negative
Subject + will not (won’t)+ have + past participle + object
1. I will not have done my homework before the class starts.
2. He will not have completed his pilot’s license by the end of the year.
3. She will not have finished her assignment by tomorrow.
4. The mechanics will not have fixed the car before our trip.
6. She won’t have finished her painting by the weekend.
6. I won’t have reviewed all the reports before our next meeting.
7. We won’t have harvested all the crops before the sun sets.
1.3 Interrogative
Will + subject + have + past participle + object + ?
1. Will you have finished your homework by the end of the day?
2. Will you have saved enough money before your wedding next year?
3. Will you have fixed the car by noon tomorrow?
4. Will you have finished reading the book by Friday?
5. Will the workers have fixed the road by tomorrow afternoon?
6. Will you have prepared lunch by 6 AM tomorrow?
7. Will the kids have slept by the time you finish cooking?
1.4 Interrogative negative
Will + subject + not + have + past participle + object + ?
1. Will he not have finished his degree by next year?
2. Will we not have saved enough money for our trip by the end of the summer?
3. Won’t they have left for the airport by 5 PM?
4. Won’t you have read the book by the end of the month?
5. Won’t they have left by the time we arrive?
6. Won’t the mechanic have fixed the car by the weekend?
I will have finished
You will have finished
He will have finished
She will have finished
It will have finished
We will have finished
You will have finished
They will have finished
I’ll have finished
You’ll have finished
He’ll have finished
She’ll have finished
It’ll have finished
We’ll have finished
You’ll have finished
They’ll have finished
1. I will have finished my yoga class by the time you come back.
2. I will have bought a car by next year.
I will not have finished
You will not have finished
He will not have finished
She will not have finished
It will not have finished
We will not have finished
You will not have finished
They will not have finished
I won’t have finished
You won’t have finished
He won’t have finished
She won’t have finished
It won’t have finished
We won’t have finished
You won’t have finished
They won’t have finished
1. I will not have finished cooking by the time the baby wakes up.
2. I will have saved enough money by the time summer starts.
Will I have finished?
Will you have finished?
Will he have finished?
Will she have finished?
Will it have finished?
Will we have finished?
Will you have finished?
Will they have finished?
Will I not have finished?
Will you not have finished?
Will he not have finished?
Will she not have finished?
Will it not have finished?
Will we not have finished?
Will you not have finished?
Will they not have finished?
1. Will the mechanics have repaired the brakes by the time we pick up the car?
2. Won’t the mechanics have assembled the new parts before the delivery truck returns?
Won’t I have finished?
Won’t you have finished?
Won’t he have finished?
Won’t she have finished?
Won’t it have finished?
Won’t we have finished?
Won’t you have finished?
Won’t they have finished?
2. Use of the future perfect tense
We use the future perfect simple to talk about an action that is predicted to happen before a specific point in the future.
1. We will have your car fixed by noon.
2. I will have published two books by December this year.
3. My father will have retired by the time I get married.
4. By the time I turn 40, I will have saved enough money to buy a house.
5. By the end of the year, inflation will have risen to an estimated rate of about 5 percent.
6. She will have made a decision on her future career plans by the time she graduates.
7. The children will have grown up and left home by the time their parents retire.
Time expressions like by the time, by then, by [specific time], and before are commonly used with the future perfect simple tense to specify the time or event we’re referring to. Even though we’re referring to a future event, the present simple tense is used after time expressions like by the time. “By the time you come back from shopping, I will have finished my homework.”
To reinforce what you’ve learned, complete this future perfect tense worksheet.
