1. Months of the year
A month usually has four weeks and a few days. Each week has exactly 7 days. February is the shortest month, with 28 days in most years and 29 days in a leap year.
2. Seasons of the year
A period of the year characterised by a specific weather condition
A rainy season, a dry season.
The coldest season of the year.
It starts when one of the earth's poles reaches its maximum tilt away from the sun
In the Northern Hemisphere, winter starts around December 21 and ends around March 21. In the Southern Hemisphere, winter begins around June 21 and ends around September 21.
In winter, the days are shorter, and the nights are longer; many plants and trees lose all of their leaves. Winter ends in spring.
The warmest season of the year.
Summer begins when one of the earth's poles reaches its maximum tilt toward the sun
In the Northern Hemisphere, summer begins around June 21 and ends around September 21. In the Southern Hemisphere, summer starts around December 21 and ends around March 21. In summer, the days are longer, and the nights are shorter.
Starts after summer and ends when winter begins
In the Northern Hemisphere, autumn starts around September 21 and ends around December 21. In the Southern Hemisphere, autumn begins around March 21 and ends around June 21.
During autumn, many leaves change colours from green to orange, yellow or red. As winter approaches, many plants and trees shed their leaves as part of a natural process to survive during the winter's harsh weather conditions.
Starts after winter and ends when summer begins
In the Northern Hemisphere, spring begins around March 21 and ends around June 21. In the Southern Hemisphere, spring begins around September 21 and ends around December 21.
As spring begins, the weather becomes warmer again, flowers bloom, trees and plants start sprouting leaves.
Can you guess which of the following pictures corresponds to which season?




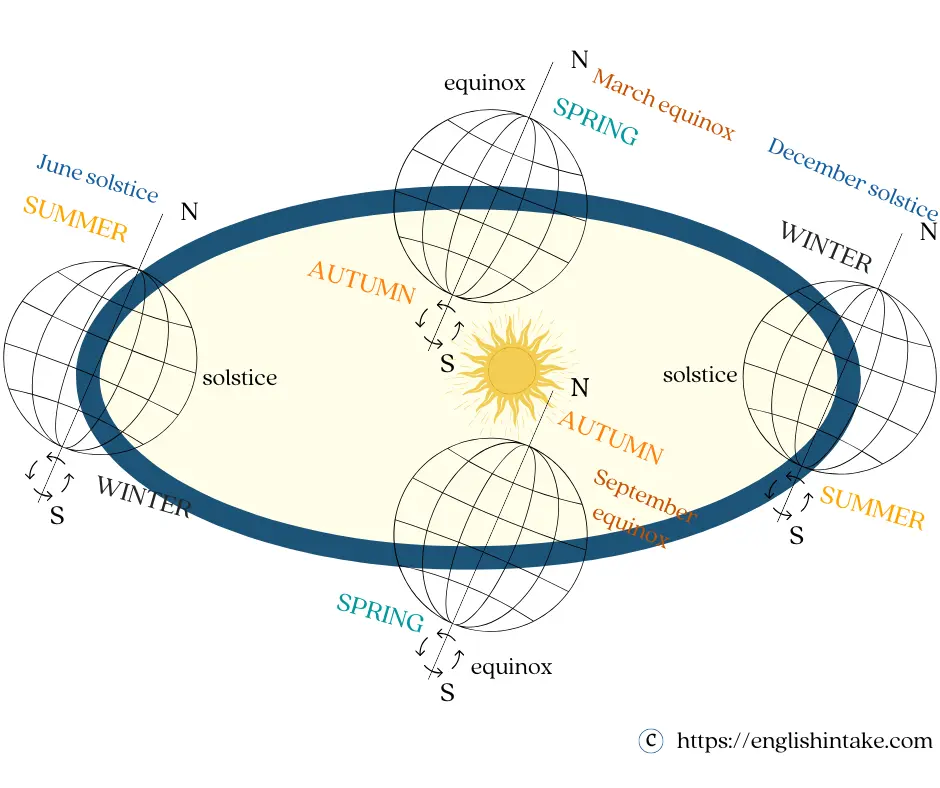
3. Why does the Earth have seasons?
The Earth rotates around itself once every 24 hours. At any given time, one side of the Earth faces the sun and receives sunlight while the other side is in complete darkness. That is why we have day and night.
The Earth makes a complete orbit around the sun every 365 days or one year. Since the Earth's spin axis is tilted at a fixed angle relative to its orbital plane, at some point along the orbit, the south pole reaches a maximum tilt away from the sun, whereas the north pole reaches a minimum tilt toward the sun. This happens during the solstice.
The part that is closer to the sun will be warmer, and this is summer. The part farther away from the sun will be colder, and this is winter.
As the Earth continues its revolution around the sun, there will be a moment when the sun passes directly above the equator, resulting in an equal length of days and nights on all parts of the Earth. This happens during the equinox.
The March equinox marks the beginning of spring in the Northern Hemisphere and autumn or fall in the Southern Hemisphere.
There are four seasons on Earth. They are called winter, spring, summer and fall (American English) or autumn (British English). Each season lasts about 3 months. The Northern and Southern Hemispheres have opposite seasons.
When it is summer in the Northern Hemisphere, it is winter in the Southern Hemisphere. When it is spring in the Northern Hemisphere, it is autumn or fall in the Southern Hemisphere.
The parts of the Earth closer to the equator experience a less dramatic temperature change than those farther away. Therefore, regions near the equator typically have two seasons, a sequence of dry and rainy seasons.
Polar regions experience a more dramatic seasonal variation. Near the poles, the amount of daylight changes substantially between summer and winter.
