1. Numbers in words in English
In this lesson, we will learn how to write numbers in words.
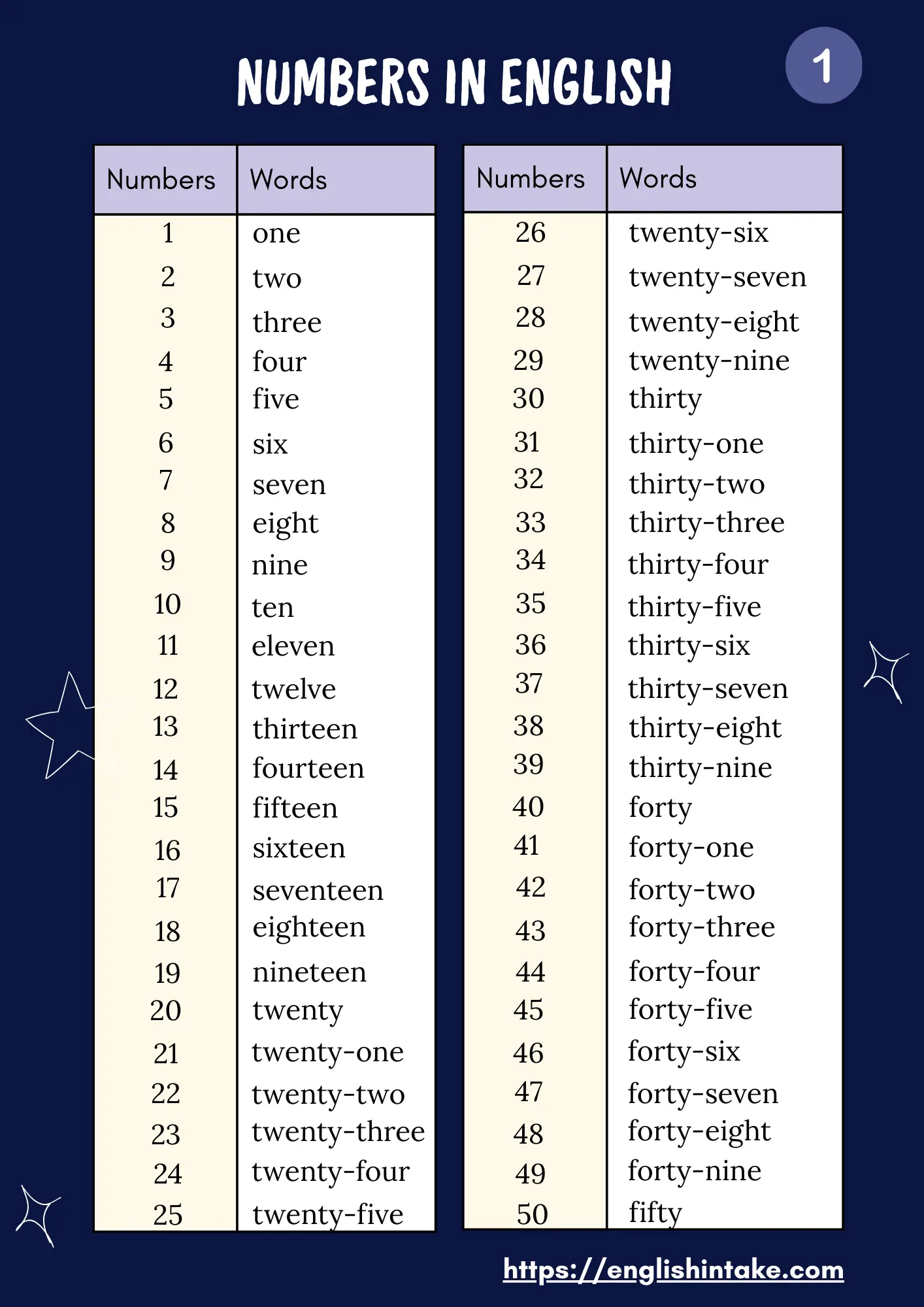
1- One
2- Two
3- Three
4- Four
5- Five
6- Six
7- Seven
8- Eight
9- Nine
10- Ten
11- Eleven
12- Twelve
13- Thirteen
14- Fourteen
15- Fifteen
16- Sixteen
17- Seventeen
18- Eighteen
19- Nineteen
20- Twenty
21- Twenty-one
22- Twenty-two
23- Twenty-three
24- Twenty-four
25- Twenty-five
26- Twenty-six
27- Twenty-seven
28- Twenty-eight
29- Twenty-nine
30- Thirty
31- Thirty-one
32- Thirty-two
33- Thirty-three
34- Thirty-four
35- Thirty-five
36- Thirty-six
37- Thirty-seven
38- Thirty-eight
39- Thirty-nine
40- Forty
41- Forty-one
42- Forty-two
43- Forty-three
44- Forty-four
45- Forty-five
46- Forty-six
47- Forty-seven
48- Forty-eight
49- Forty-nine
50- Fifty
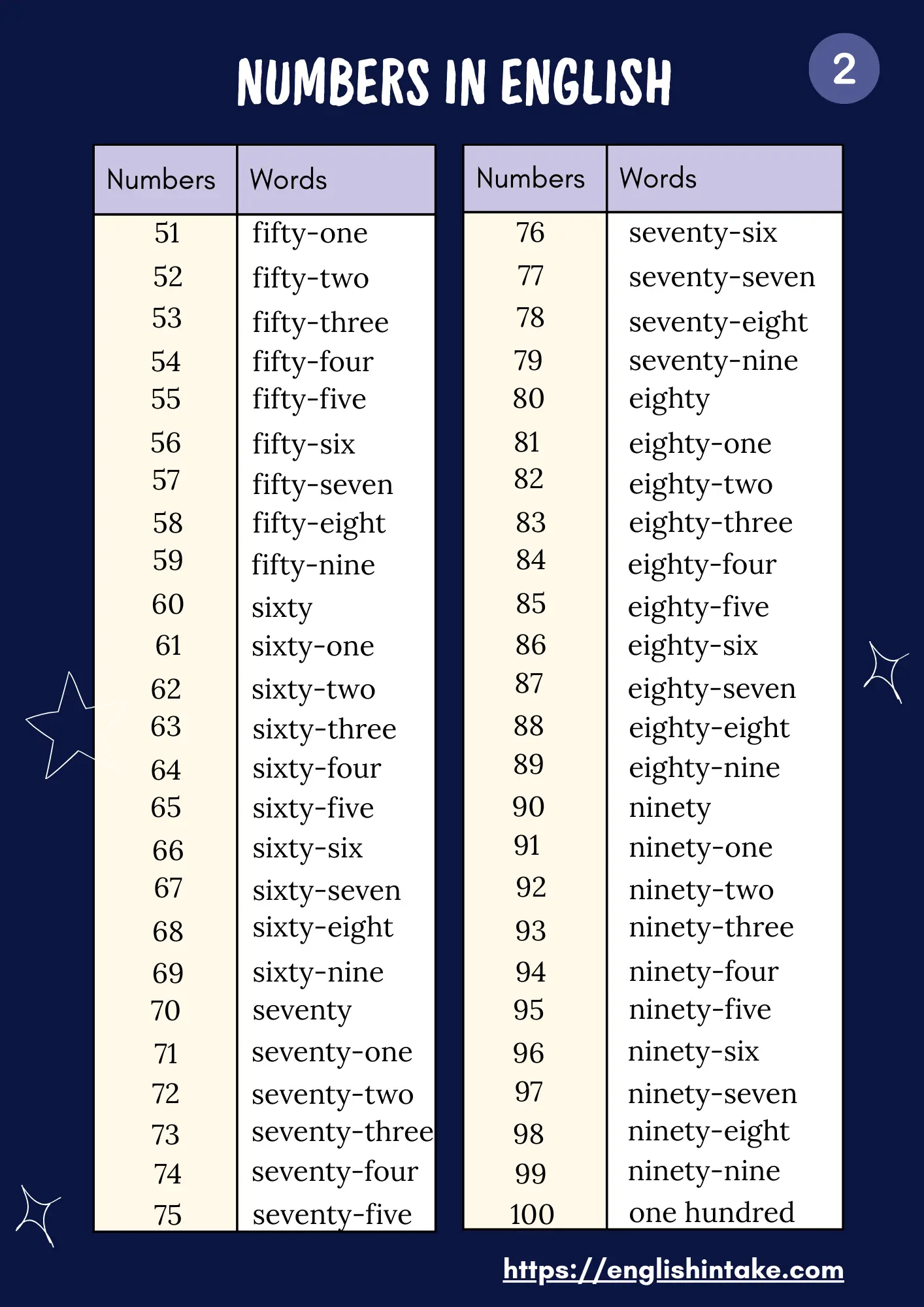
51- Fifty-one
52- Fifty-two
53- Fifty-three
54- Fifty-four
55- Fifty-five
56- Fifty-six
57- Fifty-seven
58- Fifty-eight
59- Fifty-nine
60- Sixty
61- Sixty-one
62- Sixty-two
63- Sixty-three
64- Sixty-four
65- Sixty-five
66- Sixty-six
67- Sixty-seven
68- Sixty-eight
69- Sixty-nine
70- Seventy
71- Seventy-one
72- Seventy-two
73- Seventy-three
74- Seventy-four
75- Seventy-five
76- Seventy-six
77- Seventy-seven
78- Seventy-eight
79- Seventy-nine
80- Eighty
81- Eighty-one
82- Eighty-two
83- Eighty-three
84- Eighty-four
85- Eighty-five
86- Eighty-six
87- Eighty-seven
88- Eighty-eight
89- Eighty-nine
90- Ninety
91- Ninety-one
92- Ninety-two
93- Ninety-three
94- Ninety-four
95- Ninety-five
96- Ninety-six
97- Ninety-seven
98- Ninety-eight
99- Ninety-nine
100- One hundred
2. Types of numbers in English
Cardinal
We use cardinal numbers to indicate quantity. They answer the question "How many?". Some examples include one, two, three, etc.
101- One hundred one
102- One hundred two
150- One hundred fifty
200- Two hundred
201- Two hundred one
204- Two hundred four
206- Two hundred six
250- Two hundred fifty
300- Three hundred
301- Three hundred one
305- Three hundred five
310- Three hundred ten
350- Three hundred fifty
400- Four hundred
410- Four hundred ten
425- Four hundred twenty-five
450- Four hundred fifty
500- Five hundred
600- Six hundred
700- Seven hundred
800- Eight hundred
900- Nine hundred
1,000- One thousand
2,000- Two thousand
5,000- Five thousand
10,000- Ten thousand
50,000- Fifty thousand
100,000- One hundred thousand
500,000- Five hundred thousand
1,000,000- One million
9,876,543 - Nine million, eight hundred and seventy-six thousand, five hundred and forty-three
For more practice, you can do our exercise on writing big numbers in English.
Ordinal
We use ordinal numbers to indicate rank, order, or position.
1. Barack Obama was the first African-American president of the United States.
2. Donald Trump was the forty-fifth president of the United States.
3. My brother was awarded the second-best prize at Spain's annual International Festival of Music and Dance.
4. We live on the fourth floor.
1st. first.
2nd. second.
3rd. third.
4th. fourth.
5th. fifth.
6th. sixth.
7th. seventh.
8th. eighth.
9th. ninth.
10th. tenth.
11th. eleventh.
12th. twelfth.
13th. thirteenth.
14th. fourteenth.
15th. fifteenth.
16th. sixteenth.
17th. seventeenth.
18th. eighteenth.
19th. nineteenth.
20th. twentieth.
21st. twenty-first.
22nd. twenty-second.
23rd. twenty-third.
24th. twenty-fourth.
25th. twenty-fifth.
26th. twenty-sixth.
27th. twenty-seventh.
28th. twenty-eighth.
29th. twenty-ninth.
30th. thirtieth.
40th. fortieth.
50th. fiftieth.
60th. sixtieth.
70th. seventieth.
80th. eightieth.
90th. ninetieth.
100th. hundredth.
101st. hundred and first.
1000th. thousandth.
100000th. hundred thousandth.
1000000th. millionth.
1000000000th. billionth.
Cardinal and ordinal numbers can also work as determiners in English when they come before a noun (e.g., “three chairs”, “the second floor”).
Fractional
A fraction is a way to show the parts of a whole thing. Imagine you have a pizza. If you cut it into pieces and take just a few of those, you’re taking a fraction of the pizza. The quantity at the top (numerator) says how many pieces you have, and the bottom one (denominator) tells you how many pieces the whole pizza was cut into. So, if you have 2 pieces out of 8, you write it as 2/8.
1/2 - one over two (commonly known as half)
1/3 - one over three (one-third)
2/3 - two over three (two-thirds)
1/4 - one over four (a quarter or one-fourth)
3/4 - three out of four (three-quarters or three-fourths)
1/5 - one out of five (one-fifth)
2/5 - two out of five (two-fifths)
1/6 - one over six (one-sixth)
5/6 - five over six (five-sixths)
1/7 - one out of seven (one-seventh)
1/8 - one over eight (one-eighth)
1/10 - one out of ten (one-tenth)
7/10 - seven out of ten (seven-tenths)
1/20 - one over twenty (twentieth)
47/100 - forty-seven out of a hundred (forty-seven hundredths)
1/100 - one over a hundred (a hundredth)
1/1,000 - one over a thousand (a thousandth)
Decimal

Reading rules:
- Read the decimal point as "point.
- Read decimal part individually.
- Read the whole part normally.
- Zeroes after the decimal point can be read as “zero” or “oh.”
- 12.34 ”Twelve point three four“ ✘ Incorrect: “ Twelve point thirty-four. ”
- 12.05 This can be read as “Twelve point zero five” or “Twelve point oh five.”
In certain contexts, like money, decimal numbers are read differently. For example, $3.50 might be read as “three dollars and fifty cents” instead of “three point five zero.”
3. Other types used in mathematics
IntegersThese include all whole numbers (both positive and negative) and zero: -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, etc.
RationalThey can be expressed as the quotient of two integers (a fraction) where the denominator is not zero: 1/2, -3/4, 5, 0.75, etc.
IrrationalThey cannot be expressed as a simple fraction; they have non-repeating, non-terminating decimal expansions: π (pi), √2 (the square root of 2), etc.
RealThese include all rational and irrational numbers, including integers, and fractions 3.14, -1.5, 0, 2/3, etc.
ComplexComplex numbers include a real part and an imaginary part: a + bi (e.g., 4 + 5i), where bi is the imaginary part, and a is the real part.
PrimePrime numbers are natural numbers greater than 1 that have no positive divisors other than 1 and themselves, including 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, etc.
CompositeThese are natural numbers greater than 1 that are not prime; they have positive divisors other than 1 and themselves: 4, 6, 8, 9, 12, etc.
EvenThese are integers divisible by 2: -4, 0, 2, 6, etc.
OddThese are integers not divisible by 2 like -3, 1, 5, 9, etc.
