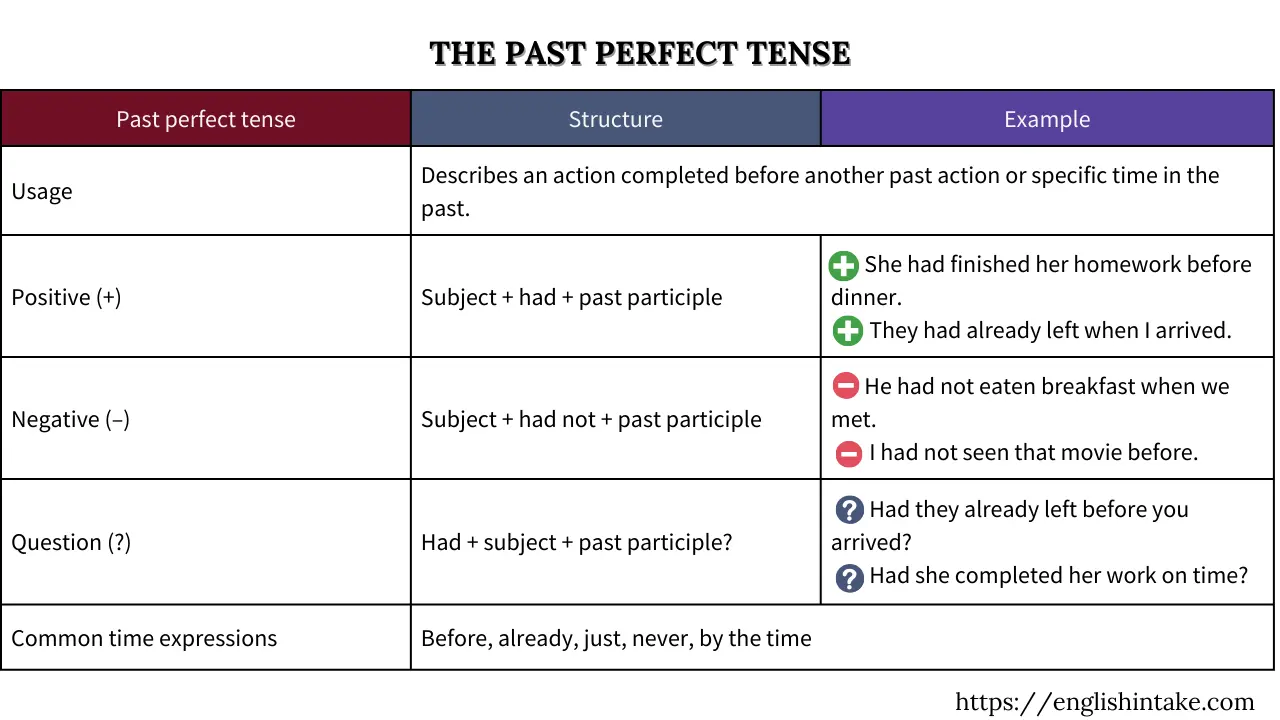
1. Form of the past perfect
The past perfect tense is formed by using the auxiliary verb had followed by the past participle of the main verb (leave => had left).
- I had left
- You had left
- He had left
- She had left
- It had left
- We had left
- You had left
- They had left
Study the text below and pay attention to the verb tenses used.
The Johnson family had never had much money until they won the lottery in 1998. Before that, they were living in a small rented apartment. They struggled to pay the bills. They rarely went on vacations. Their life changed when they bought a house. They had never lived in a big house before. The children were happy to have their own rooms for the first time. The Johnsons felt proud every time they looked at their new home. It was something they had never thought they would have one day.
2. Use of the past perfect
2.1 Sequencing past actions
The past perfect can be used to describe a completed (or uncompleted) action up to (or before) a specific point in the past.
1. I had finished my homework before I watched TV.
2. By the time I arrived at the party, everyone had already left.
3. The kids had already gone to bed by the time their grandparents arrived.
4. Many people had already left the party by the time she sang.
5. They cleaned the house after they had finished the party.
6. He was fired after the committee had issued their report.
2.2 Talking about how many times something happened before a specific point in the past.
1. We had warned him twice before we decided to fire him.
2. How many times had you tried to convince her before you finally gave up?
3. We had visited the house three times before we bought it.
4. I had read the book three times before. (The second action does not have to be indicated)
5. We had met several times before, but I had never had the courage to tell her how much I loved her.
6. We decided to start a non-profit organisation after we had visited Africa several times.
2.3 Unfulfilled hope (or wish) in the past
- I wish I had met him before he passed away.
- If only she had loved me!
- She had hoped to see you at the party, but you didn't show up.
- They had hoped to go on vacation this year, but they couldn't afford it.
- I had hoped to get a promotion at work, but my boss had other plans.
- If only the police had arrived on time!
3. Past perfect or past simple?
| Situation | Use past perfect | Use past simple |
|---|---|---|
| One action happened before another in the past | ✓ She had left before we arrived. | ✗ Incorrect |
| One completed action in the past | ✗ Incorrect | ✓ She left early. |
| Two actions happened at the same time | ✗ Incorrect | ✓ He collapsed when he heard the news. |
| A time word makes the order clear | ✓ After they had eaten, they left. | ✓ After they ate, they left. |
| "The first/second time that..." structure | ✓ It was the first time he had seen snow. | ✗ Incorrect |
We use the structure past simple + past perfect to emphasise the sequence of events. This structure is often accompanied by time expressions such as after, when, until, before, by the time, or as soon as. I had finished my homework when the power went out. The action of finishing homework was completed before the action of losing electrical power.
We use the past perfect (not the past simple) when we say it was the first / second / third etc time that because the structure indicates a connection between two particular points in the past. It was the first time that I had seen such a terrible accident.
The past simple + past simple structure is used to indicate that two actions occurred simultaneously in the past. He collapsed when he collided with another player. Here, the action of collapsing occurred at the same time as the action of colliding with another player.
If the sequence of events is clear from the context or the use of a time expression, we can use either the past simple or the past perfect tense. After the police had left (or left), they started the party again. If there is only a single event, we often use the past simple tense. He stole a car.
Read the text below to see how the past perfect tense is used to narrate past events.
In August 2023, Gabon experienced a significant political upheaval. President Ali Bongo Ondimba, who had been in power since 2009 following his father Omar Bongo's lengthy rule, was declared the winner of the August 26 general election, securing a third term. However, the election was marred by allegations of fraud and irregularities, leading to widespread protests and unrest.
In the early hours of August 30, just after the official election results were announced, a group of military officers seized control of key government institutions in the capital, Libreville. Later, they appeared on TV and said that they had taken power. They also said that they had annulled the election results, dissolved state institutions, and closed national borders. The officers cited the need to restore credibility and stability. They accused the Bongo administration of irresponsible governance that threatened to plunge the country into chaos.
The coup was led by General Brice Oligui Nguema, the head of the Republican Guard and a cousin of Ali Bongo. Following the takeover, Bongo was placed under house arrest, and several high-ranking officials were detained on charges including treason and corruption. General Nguema was subsequently named transitional president. The military claimed that they had put an end to a corrupt government. This event marked the end of the Bongo family's 56-year dominance in Gabonese politics. The international community, including the African Union, condemned the coup and called for a swift return to constitutional order.
When you feel ready to take a test, you can try this past perfect tense worksheet.
