1. What is the present continuous tense?
The present continuous or progressive tense is a verb form that describes actions happening at the moment of speaking or activities planned for the future.
2. Present continuous chart (present progressive)
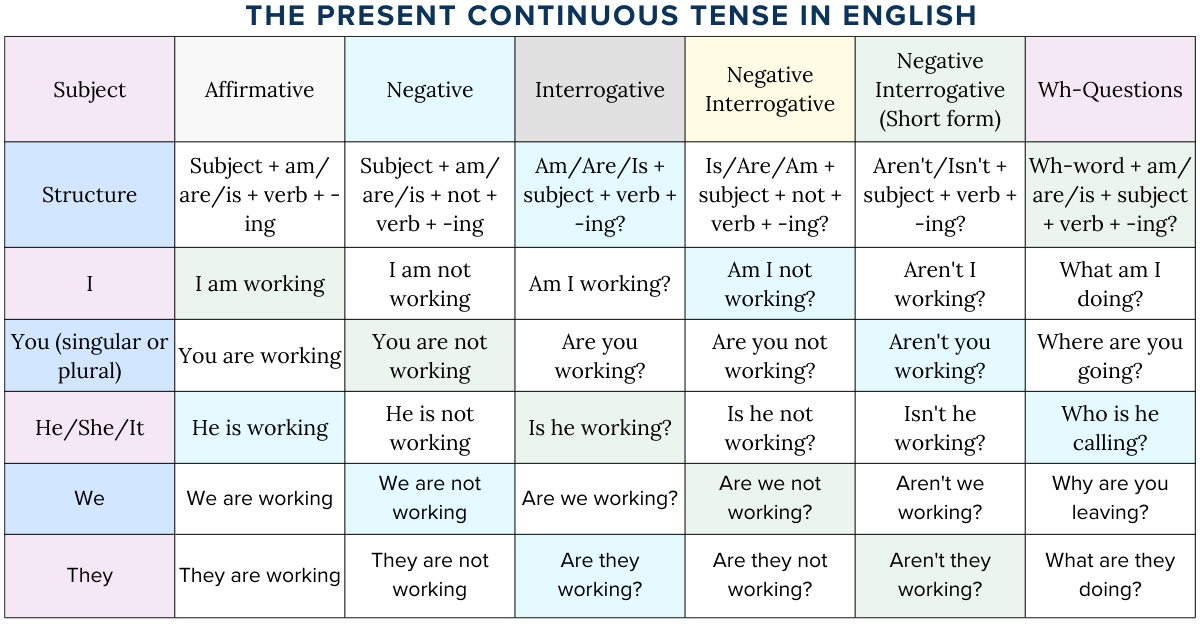
The present continuous chart above offers a comprehensive overview of how to form sentences in this tense across various subjects. It illustrates its affirmative, negative, and interrogative structures in everyday conversation.
3. Use of the present continuous tense
3.1 Talking about something that is happening at the time of speaking
We use the present progressive tense to talk about ongoing actions happening at the time of speaking, which may continue in the future.
Structure: present simple form of the verb to be + the present participle of the main verb.
N.B. To form the present participle, we add -ing to the base form of the verb, e.g., work => working, go => going.

- You are reading this sentence.
- You are learning English right now.
The following questions are frequently used in English. They mean "How are you?":
- How are you doing?
- How's it going?
- How are you getting on?
3.2 Expressing unfinished actions, which are not necessarily happening at the time of speaking
- I am looking for a job.
- Are you still working in a bank?
- I am learning Spanish.
- They are getting divorced.
- We are taking the murderer to court.
3.3 Talking about temporary situations
Temporary situations are things that are happening for a short period of time but are not permanent. Common examples include:
- Actions happening now but not permanently
- Short-term living or working arrangements
- Temporary habits or behaviours
🕛 The following time expressions are usually used to describe temporary situations:
- at the moment
- currently
- these days
- for now
- for the time being
- temporarily
- I am currently living with my parents.
- I am staying with a friend for the summer holiday.
- Allica Bank is accepting applications for the position of loan manager at the moment.
- He is drinking a lot these days.
- I am temporarily closing my Facebook account.
Let’s look at more examples to help you better understand how to use the present continuous tense for temporary situations.
🏠 Living arrangements
- I am currently living with my parents while I look for a flat.
- She is staying with her aunt for the summer.
- We are renting a house until we buy our own.
💼 Work & study situations
- Allica Bank is accepting applications for the position of loan manager at the moment.
- He is working as a waiter until he finds a permanent job.
- She is taking a short course in photography these days.
🍷 Temporary habits & behaviour
- He is drinking a lot these days.
- I am exercising more often this month.
- People are using online shopping more than ever.
🛑 Short-term decisions & changes
- I am temporarily closing my Facebook account.
- They are moving to a different city for a few months.
- The library is offering free online courses this summer.
3.4 Describing changing situations or actions in progress
We use the present continuous when:
- A situation is gradually changing (e.g., improving, worsening, increasing, decreasing).
- A process is happening right now but is not yet complete.
- Something is in motion (e.g., arrivals, departures, progress).
Common words and phrases used with changing situations:
- getting better/worse
- increasing / decreasing
- improving / declining
- changing / developing / evolving
- growing / shrinking
- at the moment / these days
Example sentences:
📈 Positive changes (improvements & growth)
- The economy is getting better. (It is improving over time.)
- Your child is growing fast. (The change is happening gradually.)
- Technology is progressing at an exponential rate. (Ongoing development.)
📉 Negative changes (decline or deterioration)
- His health condition is getting worse. (It is not stable; it is deteriorating.)
- The environment is becoming more polluted. (A continuous negative change.)
- Crime rates are increasing in some cities. (They are going up over time.)
🚆 Actions that are currently in motion
- The bus is arriving. (It is moving toward the station.)
- The weather is changing quickly today. (It is in progress.)
- The company is expanding to new countries. (The process is ongoing.)
- The economy is getting better.
- Brenda's health condition is getting worse.
- Your child is growing fast.
- Technology is progressing at an exponential rate.
- The train is arriving.
3.5 Talking about plans or intentions
We use the present progressive tense to refer to definite plans that have already been decided, such as:
- Planned events with a specific time
- Arrangements already made
- Things that are happening soon
The following time expressions are usually used in these situations:
- This evening / tonight
- Tomorrow
- This weekend
- Next week / next month
- In a few days
- I am going out this evening.
- He is leaving tomorrow.
- My grandparents are visiting us this weekend.
- I'm looking forward to our meeting tomorrow.
- They are flying to London next week.
4. The form be + going to + verb (base form)
The form am/is/are + going to + the base form of the verb is frequently used to talk about future plans and intentions.
We use be + going to in the following situations:
4.1 Talking about planned actions
We use be + going to when we have already decided to do something in the future. These are planned actions that we intend to do but may not have arranged yet.
- I am going to learn Spanish next year. (I have decided but haven't started yet.)
- We are going to move to a new apartment soon. (The decision is made.)
- She is going to start a new job next month. (She has planned it.)
🕐 Common time expressions:
- tomorrow
- next week
- next month
- next year
- Soon
- in a few days
- in the near future
- later today
- this evening
- this weekend
4.2 Making predictions based on present evidence
We use be + going to when we predict something based on what we see or we know now.
- Look at those dark clouds! It is going to rain soon. (Present evidence: dark clouds.)
- Be careful! You are going to spill your coffee. (Present evidence: cup is tilting.)
- He is going to fail the test if he doesn’t study. (Present evidence: he hasn’t studied.)
Examples of common clues for predictions:
- Weather conditions: The sky is grey, it’s going to rain.
- Personal actions: If you eat too much, you’re going to feel sick.
- Current trends: Electric cars are going to replace petrol cars.
- I am going to break up with my girlfriend.
- I am going to bed now.
- They are going to take him to court.
- We are going to sell our house.
- She is going to have her hair cut.
5. Spelling rules
In most cases, we add -ing to the base form to make the -ing form.
Examples:
| be => being | call => calling |
| say => saying | try => trying |
| think => thinking | feel => feeling |
| see => seeing | ask => asking |
| look => looking | do => doing |
| tell => telling | drink => drinking |
In general, when the verb ends in -e, we take off the -e and add -ing.
| take => taking | use => using |
| make => making | give => giving |
| have => having | rise => rising |
| become => becoming | drive => driving |
| come => coming | ride => riding |
| leave => leaving | arrive => arriving |


