1. What is a reported speech?
Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is used to communicate what someone else said without quoting them directly. This is especially useful when relaying information or telling stories. In reported speech, we often need to change the verb tense, pronouns, and time expressions.
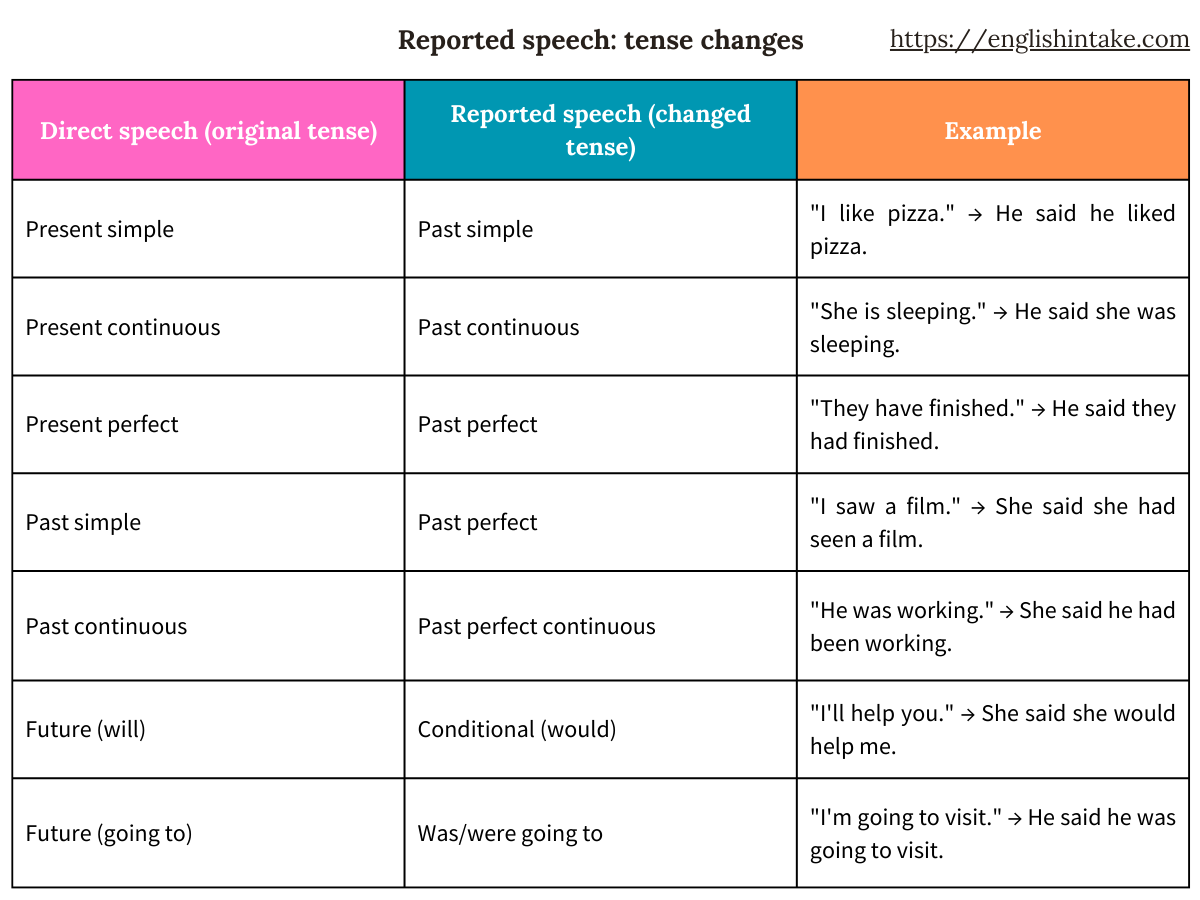
2. Tense change in reported speech
When changing from direct speech to reported speech, the verb tense usually shifts one step back.
- Simple present → Simple past
- Present continuous → Past continuous
- Simple past → Past perfect
- Present perfect → Past perfect
- Past perfect → Past perfect
- Present perfect continuous → Past perfect continuous
- Past continuous → Past perfect continuous
- Future → Present conditional
- Future continuous → Conditional continuous
The modal verbs might, could, would, should, and ought to do not change in reported speech.
2.1 Present simple
1. I love you
, he said.
He said that he loved me.
2. She seems happy today
, said Mike.
Mike said that she seemed happy that day.
3. We walk to school every day
, said the students.
The students said that they walk to school every day.
4. You are wrong
, said Jack.
Jack said that I was wrong.
5. He is guilty
, said the judge.
The judge said that he was guilty.
6. She visits her grandparents every Sunday
, said Jane.
Jane said that she visits her grandparents every Sunday.
7. I’m not in the mood for shopping today
, said Sarah.
Sarah said that she was not in the mood for shopping that day.
8. We want to hire you
, said the CEO.
The CEO said that they wanted to hire me.
9. She lacks experience for this job
, said Emily.
Emily said that she lacked experience for that job.
2.2 Present continuous
1. I am watching a movie
, she said.
She said that she was watching a movie.
2. He is cooking dinner
, said Sarah.
Sarah said that he was cooking dinner.
3. We are studying for the exam
, said the students.
The students said that they were studying for the exam.
4. She is playing the piano
, said Jane.
Jane said that she was playing the piano.
5. I am working on my project
, said Tom.
Tom said that he was working on his project.
6. We are going to Spain next week
, said Robert and his wife.
Robert and his wife said that they were going to Spain the following week.
7. I am learning to play the guitar
, said Peter.
Peter said that he was learning to play the guitar.
8. She is waiting for the bus
, said Emily.
Emily said that she was waiting for the bus.
9. I am listening to the radio
, said Dad.
Dad said that he was listening to the radio.
10. He is painting his room
, said John.
John said that he was painting his room.
2.3 Past simple
1. I bought a new car
, she said.
She said that she had bought a new car.
2. He finished his homework
, said Sarah.
Sarah said that he had finished his homework.
3. We visited the museum yesterday
, said the students.
The students said that they had visited the museum the day before.
4. She baked a cake
, said Jane.
Jane said that she had baked a cake.
5. I found my lost wallet
, said Tom.
Tom said that he had found his lost wallet.
6. They went to the concert
, said the parents.
The parents said that they had gone to the concert.
7. I painted the house
, said Peter.
Peter said that he had painted the house.
8. She moved to New York
, said Emily.
Emily said that she had moved to New York.
9. We got married last year
, said the couple.
The couple said that they had gotten married the previous year.
10. I broke my leg
, said John.
John said that he had broken his leg.
2.4 Present perfect
1. I have finished my homework
, she said.
She said that she had finished her homework.
2. I have worked here for 10 years
, said Sarah.
Sarah said that she had worked there for 10 years.
3. We have completed the project
, said the students.
The students said that they had completed the project.
4. She has learned her lesson
, said Jane.
Jane said that she had learned her lesson.
5. I have found my lost wallet
, said Tom.
Tom said that he had found his lost wallet.
6. They have started a new business
, said Robert and his colleagues.
Robert and his colleagues said that they had started a new business.
7. I have met the president
, said Peter.
Peter said that he had met the president.
8. J. K. Rowling has written a new novel
, said Emily.
Emily said that J. K. Rowling had written a new novel.
9. We have climbed Mount Everest
, said the couple.
The couple said that they had climbed Mount Everest.
10. I have won a gold medal
, said John.
John said that he had won a gold medal.
2.5 Past perfect
1. I had already eaten dinner
, she said.
She said that she had already eaten dinner.
2. John had left the party early
, said Sarah.
Sarah said that John had left the party early.
3. We had finished our exams
, said the students.
The students said that they had finished their exams.
4. They had just finished dinner
, said Jane.
Jane said that they had just finished dinner.
5. He had booked the tickets
, said Jimmy.
Jimmy said that he had booked the tickets.
6. I had made a mistake
, said Peter.
Peter said that he had made a mistake.
7. She had visited her grandparents
, said Emily.
Emily said that she had visited her grandparents.
8. We had bought a house
, said the couple.
The couple said that they had bought a house.
9. He had returned the book
, said John.
John said that he had returned the book.
2.6 Present perfect continuous
1. I have been working on this project for months
, she said.
She said that she had been working on the project for months.
2. He has been learning Spanish
, said Sarah.
Sarah said that he had been learning Spanish.
3. We have been studying for the test
, said the students.
The students said that they had been studying for the test.
4. She has been cleaning the house for hours
, said Jane.
Jane said that she had been cleaning the house for hours.
5. I have been searching for my keys
, said Tom.
Tom said that he had been searching for his keys.
6. We have been organising trips for decades
, said the travel agency.
The travel agency said that they had been organising trips for decades.
7. I have been writing a book
, said Peter.
Peter said that he had been writing a book.
8. She has been practising the piano
, said Emily.
Emily said that she had been practising the piano.
9. I have been training for the marathon
, said Mark.
Mark said that he had been training for the marathon.
10. I have been working in New York for years
, said John.
John said that he had been working in New York for years.
2.7 Past continuous
1. I was studying for my exam
, she said.
She said that she had been studying for her exam.
2. I was working in the office when I heard you call my name
, said Sarah.
Sarah said that he had been working in the office when she heard me call her name.
3. We were playing football
, said the students.
The students said that they had been playing football.
4. "She was cleaning the house", said Jane.
Jane said that she had been cleaning the house.
5. I was looking for my wallet
, said Tom.
Tom said that he had been looking for his wallet.
6. They were discussing the project
, said the parents.
The parents said that they had been discussing the project.
7. I was painting the room
, said Peter.
Peter said that he had been painting the room.
8. She was visiting her aunt
, said Emily.
Emily said that she had been visiting her aunt.
9. We were hiking in the mountains
, said the couple.
The couple said that they had been hiking in the mountains.
10. He was watching the game
, said John.
John said that he had been watching the game.
Sarah said that he had been working in the office when she heard me call her name, we did not change the past simple tense to past perfect tense because the sequence of the event is clear.
2.8 Future simple
In reported speech, the future simple tense changes from will + verb to would + verb when the reporting verb is in the past.
1. I will call you tomorrow
, she promised.
She promised that she would call me tomorrow.
2. I will finish the project soon
, said Sarah.
Sarah said that she would finish the project soon.
3. We will study for the test
, said the students.
The students said that they would study for the test.
4. I will cook dinner tonight
, said Jane.
Jane said that she would cook dinner that night.
5. I will leave early today
, said Tom.
Tom said that he would leave early that day.
6. They will plan the trip
, said the parents.
The parents said that they would plan the trip.
7. I will write a book someday
, said Peter.
Peter said that he would write a book someday.
8. She will practice the piano every day
, said Emily.
Emily said that she would practice the piano every day.
9. I will train for the marathon
, said Robert.
Robert said that he would train for the marathon.
10. I will live in New York one day
, said John.
John said that he would live in New York one day.
2.9 Future continuous
1. She said I’ll be using the car next Friday
.
She said that she would be using the car the following Friday.
2. He said I’ll be studying for the exam tomorrow
.
He said that he would be studying for the exam the following day.
3. They said We’ll be flying to New York next week
.
They said that they would be flying to New York the following week.
4. She told me, I’ll be starting my new job on Monday
.
She told me that she would be starting her new job the following Monday.
5. Mike said I’ll be going on a date this weekend
.
Mike said that he would be going on a date that weekend.
6. Linda said I’ll be baking a cake for the party
.
Linda said that she would be baking a cake for the party.
7. Tom said I’ll be watching the game with my friends
.
Tom said that he would be watching the game with his friends.
8. Jane said I’ll be attending the conference in June
.
Jane said that she would be attending the conference in June.
9. He told me, I’ll be visiting my parents this weekend
.
He told me that he would be visiting his parents that weekend.
10. They said We will be painting the house next month
.
They said that they would be painting the house the following month.
3. Changing time and place references
- here → there
- tomorrow → the next/following day
- ago → before
- now → then
- next week / month / year) → the following week / month / year)
- last week / month / year) → the previous week / month / year)
- tomorrow → the next day / the following day
- yesterday → the day before
- today → that day
- tonight → that night
- the day before yesterday → two days before
- the day after tomorrow → in two days time / two days later
- at the present → at the time
- in one hour → one hour later
- in two months → two months later
- this → that
- this week / month / year etc. → that week / month / year etc.
1. She said I saw him today
.
She said that she had seen him that day.
2. He said I was there yesterday
.
He said that he had been there the day before.
3. They said We’ll go tomorrow
.
They said that they would go the next day.
4. She told me, I’ll be back next week
.
She told me that she would be back the following week.
5. Mike said I went on a trip last month
.
Mike said that he had gone on a trip the previous month.
6. Linda said I moved here three years ago
.
Linda said that she had moved there three years before.
7. Tom said I left my keys here
.
Tom said that he had left his keys there.
4. Interrogative sentences
1. He asked, Where is the library?
He asked where the library was.
2. She said, When does the train arrive?
She asked when the train arrived.
3. They asked, What time is the meeting?
They asked what time the meeting was.
4. Mike asked, Can you help me with this project?
Mike asked if I could help him with the project.
5. Linda wondered, Why is he late?
Linda wondered why he was late.
6. Tom asked, Did you finish the report?
Tom asked whether I had finished the report.
7. Jane inquired, Have they submitted the proposal?
Jane inquired if they had submitted the proposal.
8. He asked, Are you attending the conference?
He asked whether I was attending the conference.
9. They wondered, Who left the door open?
They wondered who had left the door open.
10. He asked, Is it noisy here in summer?
He asked if it was noisy there in summer.
11. Can you walk?
, Jack asked me.
Jack asked me if I could walk.
12. She asked, Do they know about the change in plans?
She asked if they knew about the change in plans.
5. How to change pronouns in reported speech?
The first-person pronouns (I, me, we, us, our, mine, ours) usually change to match the speaker in reported speech.
1. She said, I love this movie.
→ She said that she loved that movie.
2. She said, This is our car
. → She said that was their car.
The second-person pronouns (you, your, yours) typically change to match the listener in reported speech.
1. He told me, You should visit Paris.
→ He told me that I should visit Paris.
2. He said, The gift is yours.
→ He said that the gift was mine.