1. What are narrative tenses?
Narrative tenses are verb forms we use to talk about the past. They help us tell stories, describe past events, or share personal experiences. These tenses allow us to create a clear timeline of events and make our stories more engaging.
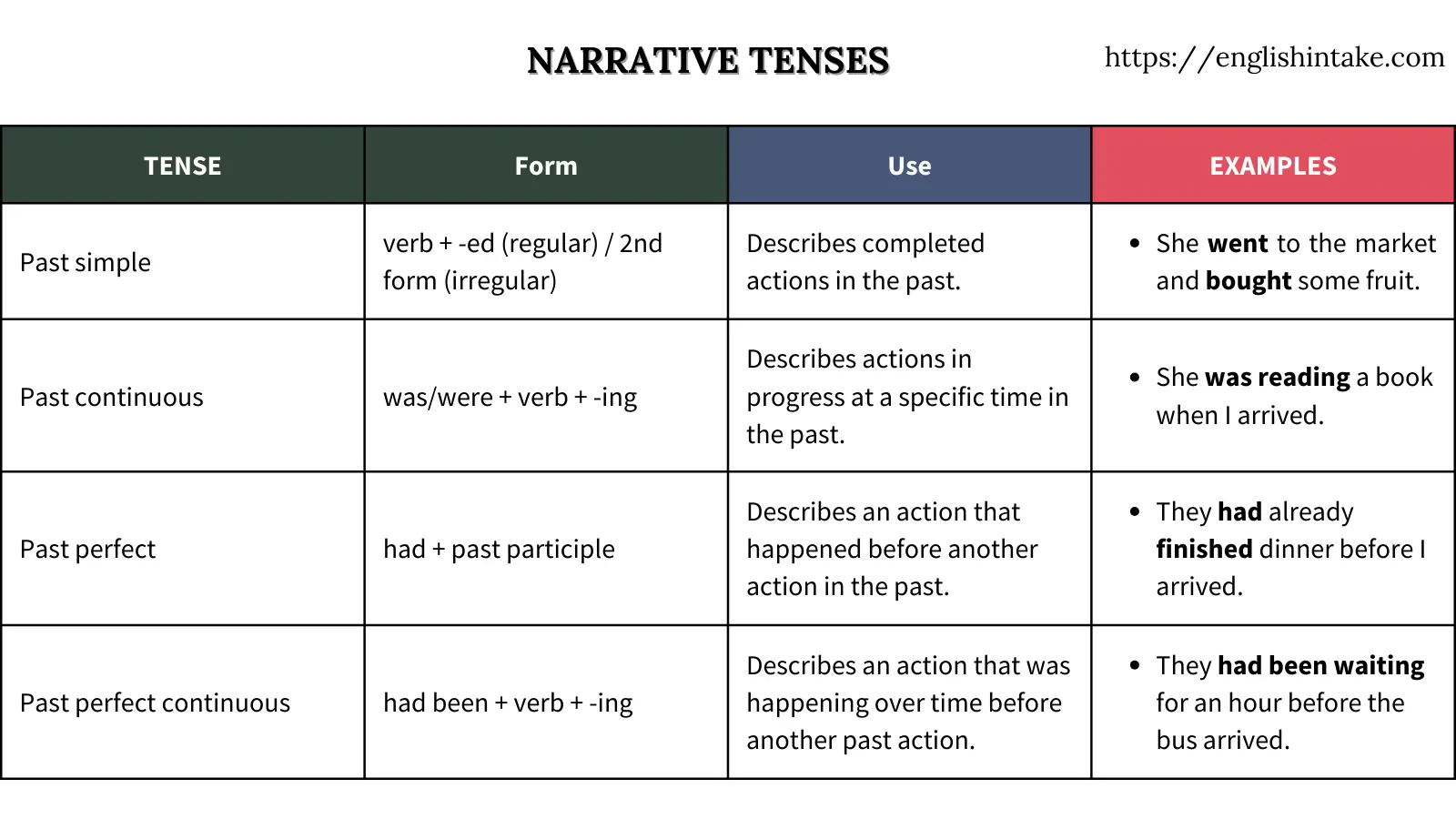
2. The four forms of narrative tenses in English
The four main forms of narrative tenses in English are:
- Past simple
- Past continuous
- Past perfect
- Past perfect continuous
We usually use one or more of these tenses in a single sentence to describe past events in detail.
Example: "I was walking (past continuous) along the beach when I saw (past simple) a strange object in the sand. I quickly realised that the tide had washed (past perfect) it ashore. It had been lying (past perfect continuous) there for hours, covered in seaweed."
2.1 Past simple
The past simple is used for actions that started and finished in the past. It’s commonly used to describe a series of events or actions in a story.
Example: "Last summer, I visited Paris. I saw the Eiffel Tower, ate croissants, and took a boat ride on the Seine River."
Form: Subject + past tense verb (e.g., visited, saw, ate).
2.2 Past continuous
The past continuous is used to describe actions that were in progress at a specific time in the past. It’s often used to set the scene or provide background information.
Example: "I was reading a book when the phone rang."
Form: Subject + was/were + verb-ing (e.g., was reading, were playing).
2.3 Past simple + past continuous
We usually use the past simple and past continuous together when one action interrupts another.
Example: "I was cooking dinner when the doorbell rang."
2.4 Past perfect
The past perfect is used to describe an action that was completed before another action or time in the past. It helps show the order of events.
Example: "By the time we arrived at the cinema, the film had already started."
Form: Subject + had + past participle (e.g., had started, had finished).
2.5 Past perfect continuous
The past perfect continuous is used to describe an action that had been ongoing for a period of time before another action or time in the past. It emphasises the duration of the action.
Example: "She had been working at the company for ten years before she got promoted."
Form: Subject + had been + verb-ing (e.g., had been working, had been studying).
3. Linking words in narratives
When telling a story, we often use linking words or phrases to connect sentences or clauses. This makes the narrative flow more naturally and keeps the reader engaged. Some common linking phrases include:
- First of all…
- Then…
- Next…
- Finally…
- After that…
- All of a sudden…
Example: "First of all, I woke up late. Then, I rushed to get ready. All of a sudden, I realised I had forgotten my keys!"
4. Useful resources
- https://englishintake.com/learn-english/lesson-past-simple/
- https://englishintake.com/learn-english/lesson-past-continuous/
- https://englishintake.com/learn-english/lesson-past-perfect/
- https://englishintake.com/learn-english/lesson-past-perfect-continuous/
- https://www.bbc.co.uk/learningenglish/course/intermediate/unit-20/tab/grammar
