1. What are prepositions of time?
Prepositions of time are words that link a noun, pronoun, or phrase to another part of a sentence to indicate a specific period when an action takes place.
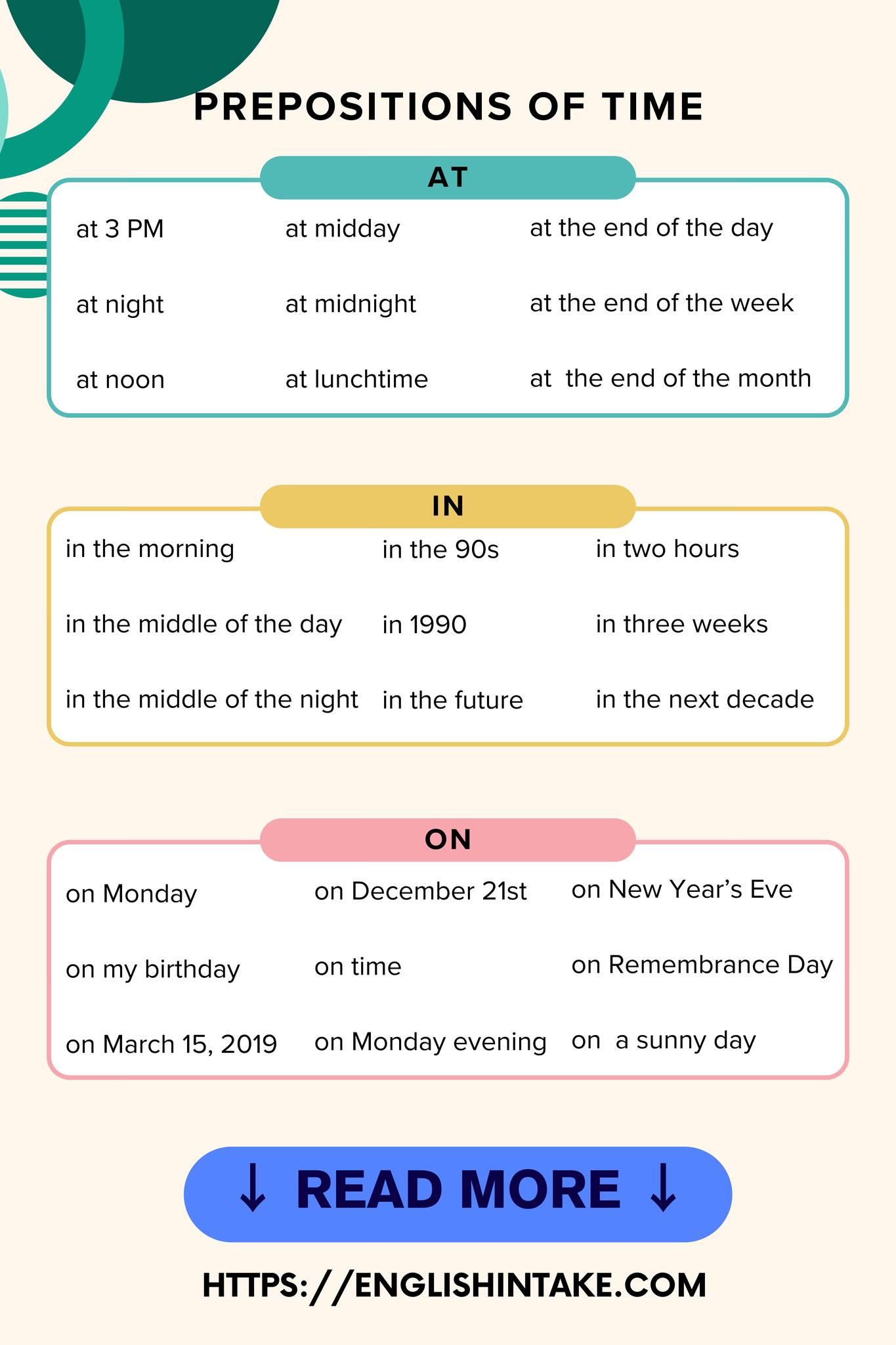
2. List of prepositions of time
Below is a list of common prepositions of time in English.
- at
- in
- on
- during
- for
- since
- until
- before
- after
- by
3. Usage
3.1. Points in time
We use at, on, and in to specify exact moments. They are used to answer "When questions".
- She will meet us at noon.
- The store opens on Monday.
- They graduated in 2020.
3.1.1. 'At' in a sentence
We use at to indicate a precise time or to refer to a specific point in time. In addition, we use at before the words the weekend.
Precise time
at 8 AM
I have a meeting at 8 AM.
at 2 PM
We’ll meet at 2 PM.
at 6 o’clock
The train leaves at 6 o’clock.
Specific points in time
at noon
She has lunch at noon.
at midday
Shops close at midday on Sundays.
at lunchtime
I’ll call you at lunchtime.
at night
I don’t like driving at night.
at midnight
People celebrate at midnight on New Year’s Eve.
at the end of the week
He’s travelling at the end of the week.
at the end of the month
I’m paid at the end of the month.
at the end of the year
We get a bonus at the end of the year.
at the end of the day is an idiom. We use it to express a final conclusion or outcome of a long or complicated process. We often say at the end of the day before talking about what we think is the most important thing about a situation.
Examples
I know it’s hard to make a decision, but at the end of the day, you have to do what feels right for you. → This means that, ultimately, the decision should be based on your own feelings and intuition.
At the end of the day, it’s important to prioritise your health above everything else. → This means that, regardless of external pressures or expectations, taking care of your well-being should be your top priority.
Before the weekend
at the weekend
We’re having a barbecue at the weekend.
We do not use any preposition before “this weekend”.
Examples
- Le’s go to the beach this weekend.
- Somebody is going to clean the house this weekend.
- My parents is visiting me this weekend.
- What are you doing this weekend?
3.2.2 'In' in a sentence
We use in for durations, parts of the day, months, seasons, years, decades, centuries, and some points in time.
Time duration
in three minutes
I’ll be ready in three minutes.
in two hours
Let’s meet in two hours.
in six days
We’ll arrive in six days.
in three months
The project finishes in three months.
in two years
She graduates in two years.
in a moment
I’ll join you in a moment.
in an instant
Her mood changed in an instant.
in a second
I’ll be with you in a second.
Different parts of the days
in the morning
I study best in the morning.
in the afternoon
We have class in the afternoon.
in the evening
Let’s talk in the evening.
in the middle of the day
We’ll meet in the middle of the day.
in the middle of the night
A noise woke me in the middle of the night.
Months
in January
I’m travelling in January.
in February
He was born in February.
in March
We celebrate St. Patrick’s Day in March.
in April
The course starts in April.
in December
It rains a lot in December.
Seasons
in winter
It’s cold in winter.
in spring
Flowers bloom in spring.
in summer
We travel in summer.
in autumn
Leaves turn red in autumn.
Years
in 1969
Neil Armstrong walked on the moon in 1969.
in 1989
The Berlin Wall fell in 1989.
in 2019
COVID-19 emerged in 2019.
Specific decades
in the 1970s
Punk rock grew in the 1970s.
in the 1980s
London changed rapidly in the 1980s.
in the 1990s
Many tech giants began in the 1990s.
Centuries
in the 15th century
Gutenberg revolutionised printing in the 15th century.
in the 19th century
Darwin published his theory in the 19th century.
in the 21st century
We live in the 21st century.
Points in time
in the past
People wrote letters in the past.
in the future
Space tourism may expand in the future.
in the distant past
Dinosaurs lived in the distant past.
in the near future
We’ll upgrade the app in the near future.
in the distant future
Humans might live on Mars in the distant future.
3.2.2 'On' in a sentence
Use on with days, days + parts of days, dates, and special days.
Days of the week
on Monday
I have an appointment on Monday.
on Tuesday
She visits on Tuesday.
on Wednesday
The concert is on Wednesday.
on Thursday
We meet on Thursday.
on Friday
The deadline is on Friday.
on Saturday
I work out on Saturday.
on Sunday
We rest on Sunday.
Days + parts of days
on Monday morning
The call is on Monday morning.
on Tuesday afternoon
There’s a talk on Tuesday afternoon.
on Wednesday evening
We’re leaving on Wednesday evening.
on Friday mornings
I have yoga on Friday mornings.
Dates
on the 1st of June
The exam is on the 1st of June.
on March 15, 2019
He arrived on March 15, 2019.
on December 21st
The solstice is on December 21st.
Use in for month + year (e.g., “in October 2023”) and on for a specific day/date.
Special days
on Valentine’s Day
We celebrate on Valentine’s Day.
on New Year’s Eve
Let’s party on New Year’s Eve.
on Christmas Day
They visit family on Christmas Day.
on my birthday
I got many gifts on my birthday.
on St. Patrick’s Day
We wear green on St. Patrick’s Day.
on Remembrance Day
People wear poppies on Remembrance Day.
A poppy is a bright red flower worn to honour those who died in military service.
3.2. Duration
We use for, since, throughout, and during to indicate how long something continues.
- The project ran for three months.
- He has been living here since 2018.
- The construction will continue throughout the summer.
- He was sleeping during the entire movie.

3.2.1. During
During can cover an entire period or part of it; it doesn’t specify exact length.
Covering the entire duration of a specific period
during the day
Shops stay open during the day.
during the night
Temperatures drop during the night.
during the summer
The park is crowded during the summer.
during the winter
It snows often during the winter.
during the Second World War
Many people died during the Second World War.
Although we say from October to December, it is the words renovation period that dictate the use of the preposition during.
Covering a portion of time between the beginning and end of a specific period
during the party
I lost my keys during the party.
during the movie
He fell asleep during the movie.
during the night
We had a power cut during the night.
during the meeting
Please don’t talk during the meeting.
Sometimes it’s unclear whether the event covers the whole period or only part of it.
3.2.2. For
We use the preposition for to indicate the duration of an action or event.
- We have been waiting for you for two hours.
- They have been dating for five years.
- We will be away for a week.
- She has been sick for two weeks.
- They have been working on the project for months.
- He has been working in the company for over a year.
- The UK has been a constitutional monarchy for many years.
- Queen Elizabeth II was in the throne for several years.
3.2.3. Since
The preposition since refers to a period of time starting at a specific point in the past and continuing up to a later point, which may be the present.
- They have been married since 2010.
- They have been friends since childhood.
- He has been playing the guitar since he was 10 years old.
- I have been working here since last year.
- We have been waiting for him since 8:00 am.
- She has been studying English since high school.
- Sarah has not been working since she had an accident.
- Sarah had an accident last year. Since then, she has not been working.
- It had been years since she had left school.
- She has been living alone since the death of her husband.
3.3 Frequency
We use every, once, and on to specify how often something occurs. They indicate habits. Let's study the examples below.
- They meet every Friday.
- The train arrives once a day.
- We see them on weekends.
3.4. Sequence and order
We use after, before, between, and by to help place events in order relative to each other.
- Let's eat after the meeting.
- The group went for coffee before class.
- They came between 5 and 6 PM.
3.4.1. Examples of 'before' in a sentence
We use the preposition before to introduce an action happening later than another action. For example, in the sentence “Before you go out, make sure to close the window.”, the action of going out is happening later than the action of closing the window. First, you close the window, then you go out. We also use the preposition before to introduce a time reference before which an action or event happens.
- We need to get ready before noon.
- The coffee shop closes at 8 PM, so we need to get there before then.
- Before the invention of the internet, people used books to find information.
- Please close the door before you leave.
- Please arrive at the airport at least two hours before your flight.
- Before you go to bed, make sure to brush your teeth and wash your face.
3.4.2. Using the preposition 'after' in a sentence
We use 'after' to introduce an action happening earlier than another action. For example, in the sentence “I took a long nap after running a marathon yesterday.”, the action “running a marathon” happens earlier than “taking a nap”. First, you run a marathon, then you take a long nap. We also use the preposition after to introduce a time reference after which an action or event happens.
- The coffee shop closes after 8 PM on weekdays.
- I’ll call you back after the meeting.
- I like to take a nap after lunch.
- My eyes feel tired after watching a movie.
- We went out for a drink after the game.
- I cried after reading the book.
- After a long thought, I finally made a decision.
3.4.3. Using 'by' in a sentence
The preposition "by" means not later than. For example, the sentence “I need to send a report by July 22nd.” means that the report must be sent before July 22nd or on July 22nd at the latest.
- We need to be at the airport by 7 PM.
- Can you let me know by Friday if you want to come to the party or not?
- Please return the book by the due date.
- The package should arrive by> the end of the week.
- Please be at the office by 9 AM tomorrow.
- By the time I got to the station the bus had already left. (=The bus left before I got to the station.)
- You need to finish your homework by lunchtime.
3.5. Approximate time
We use around, about, and by to suggest an approximate period.
- He called around midnight.
- The package arrived about noon.
- We finished by early evening.
3.6. Boundaries in time
To specify a time frame with starting and/or ending points, we use until, since, and from.
- I can work until 5 PM.
- She has lived here since last year.
- He was out from 9 to 11 AM.
3.6.1. Examples of 'until' in a sentence
Until can function as a preposition and a conjunction. It’s a preposition when it marks the time a situation continues to (e.g., We will wait until noon). It’s a conjunction when it links clauses (e.g., I will stay here until you return). In informal writing it’s often shortened to till or ’til.
Until as a preposition of time (up to)
until 8 AM
The café is open until 8 AM on weekdays.
until 2 PM
I’ll be working until 2 PM.
until dusk
We played chess until dusk.
until dawn
The lights stayed on until dawn.
until July next year
She’ll be in London until July next year.
until the end of the month
Please wait for confirmation until the end of the month.
We often use from … until to show when something starts and when it ends.
3.6.2 Using “from … until”
from 8 AM until 11 AM
The coffee shop is open from 8 AM until 11 AM on weekends.
from 7 AM until 8 PM
It’s open from 7 AM until 8 PM on weekdays.
from July 1st until July 10th
I’ll be on holiday from July 1st until July 10th.
from dusk until dawn
We had a party from dusk until dawn.
from mid-December until the end of January
The school is closed from mid-December until the end of January.
“From 8 AM until 11 AM” is equivalent to “from 8 AM to 11 AM.”
3.7. Occasions or events
To link actions to specific occasions (cultural, traditional, or life events), we use on, during.
- They get together on Christmas.
- We celebrate during the festival.
- She called on her birthday.
3.8. Continuous time
To express an event that spans a continuous time period, we use through, throughout, and until.
- He worked through the night.
- The lights are on throughout the evening.
- She stayed up until sunrise.
3.9. Deadline
We use by, and before to specify when something is due.
- The report is due by Monday.
- Submit your application before noon.
- They hoped to arrive by sunset.
3.10. Life periods
We use in, and during to describe events that took place during specific life periods.
- My grandparents lived in the 1950s.
- She was born during the winter.
- He travelled in his early twenties.
If you have enjoyed reading this post, check my lesson on the other types of prepositions in English.
