Table of contents
- 1. What are prepositions?
- 2. Types of prepositions
- 3. List of prepositions
- 3.1 Simple preposition list
- 3.2 Compound preposition list
- 4. Positions in sentences
- 4.1. At the beginning of a prepositional phrase
- 4.2. In the middle of a sentence
- 4.3. At the end of a sentence
- 4.4. Before relative pronouns
- 4.5. In phrasal verbs
1. What are prepositions?
Prepositions are words that show relationships between different elements in a sentence, such as nouns or pronouns, to other words to indicate direction, place, time, cause, manner, and possession. In this guide, you will learn all you need to know about prepositions.
2. Types and examples of prepositions
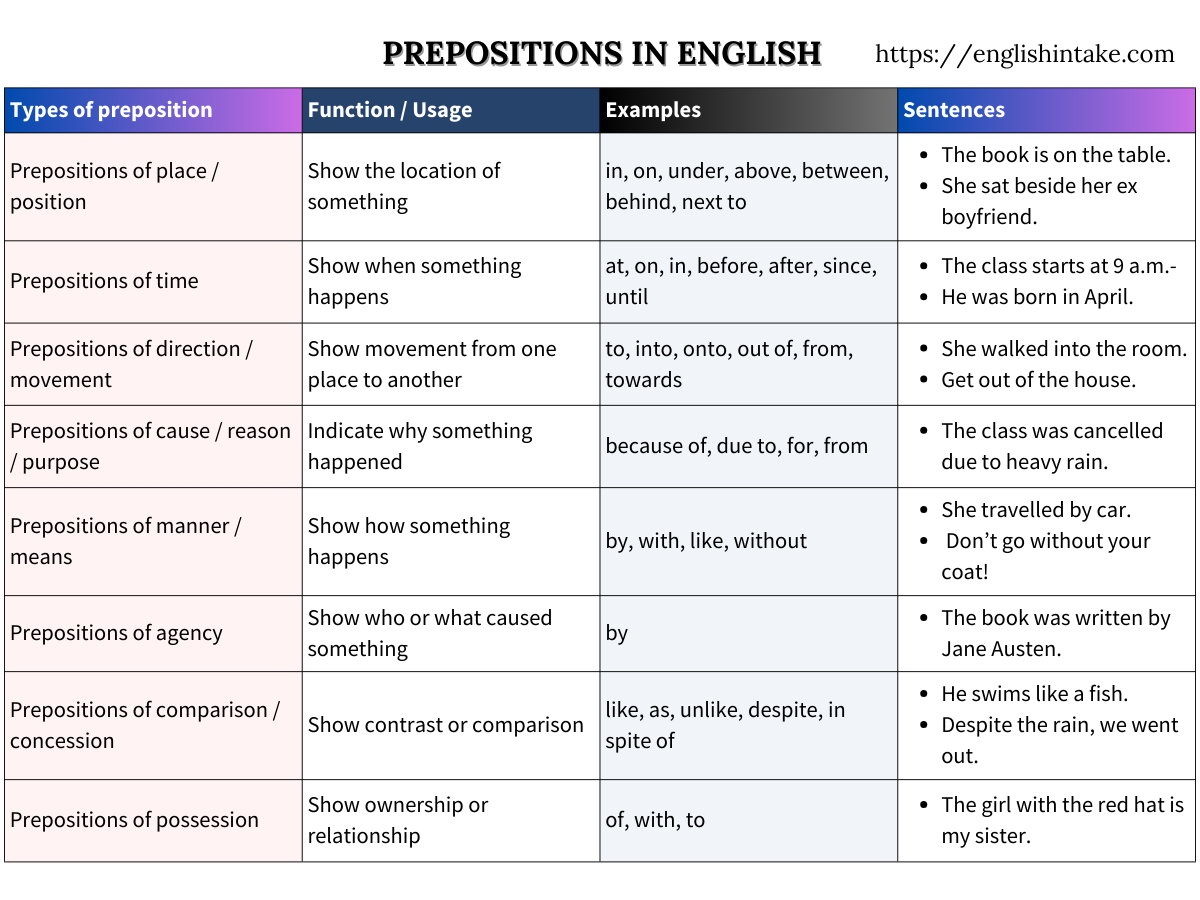
There are different types of prepositions in English, each having their role in sentences. The most common types of prepositions are:
Prepositions of placedescribe where something is located.
1. The keys are on the table.
2. The cat is under the bed.
3. I live at 18 Main Street.
Prepositions of timespecify when something happens.
1. The meeting is at 3 p.m.
2. I was born in July.
3. We will leave on Monday.
Prepositions of directionindicate movement towards a place.
1. She ran into the room.
2. He walked towards the station.
3. They drove through the tunnel.
Prepositions of mannerdescribe how something is done.
1. He travelled by car.
2. She painted the wall with a brush.
3. They fought like warriors.
Prepositions of cause or purposeexplain why something happens.
1. She was punished for lying.
2. He died of old age.
3. They fled because of the storm.
Prepositions of possessionshow ownership or association.
1. This is the house of my dreams.
2. That book belongs to Sarah.
3. He’s a friend of mine.
3. List of prepositions
3.1 Simple preposition list
- about
- above
- across
- after
- against
1. It’s a nice book about marine life.
2. Can you remove the lamp hanging above the table in the living room?
3. I saw something walking across the bridge.
4. Meet me after lunch.
5. Don’t lean your bike against the wall.
- along
- amid
- among
- anti
- around
6. Do you see that beautiful girl walking with a dog along the river? She is my girlfriend.
7. Public transport in many cities operated with limited capacity amid the COVID-19 pandemic.
8. Our online course is popular among young freelancers seeking remote work opportunities.
9. The preposition anti is rarely used; we usually say 'against' instead. Many students are anti the new rules.
10. My dream is to make a trip around the world one day
- as
- at
- before
- behind
- below
11. My wife works as a guide.
12. I did my PhD at the University of Cape Town.
13. Wash your hands before dinner.
14. There is a garden behind the house.
15. Yesterday, the temperature dropped below zero degrees.
- beneath
- beside
- besides
- between
- beyond
16. The police found dead bodies beneath the building. Beneath is usually used in formal writing. It is rarely used in informal speaking.
17. Sit beside me.
18. Do you know the difference between besides and beside? 'Beside' means 'next to'. 'Besides' means 'in addition to'. Besides the report I sent you, do you need anything else?
19. The café is between the bank and the post office.
20. I don’t want to buy things beyond my budget.
- but
- by
- concerning
- considering
- despite
21. Everyone but John agreed.
22. The letter was written by Maria.
23. I have a question concerning your invoice.
24. Considering the weather, they had to drive slowly.
25. He was not angry despite the delay.
- down
- during
- except
- excluding
- following
26. Who are these people running down the hill?
27. Nobody should use a mobile phone during my class.
28. I’m all day next week except Friday afternoon.
29. The price is €10, excluding tax.
30. Following the poor European election results of June 9th, President Emmanuel Macron dissolved the National Assembly and called for new legislative elections.
- for
- from
- in
- inside
- into
31. This gift is for you.
32. I think the bullet came from the north.
33. She lives in Valencia.
34. Stay inside the car.
35. Can you pour the milk into the bowl?
- like
- minus
- near
- of
- off
36. Jack swims like a fish.
37. The bag weighs three kilos minus the straps.
38. Our house is near the train station.
39. A cup of tea would be nice.
40. Can you take your feet off the sofa, please?
- on
- onto
- opposite
- outside
- over
41. The keys are on my desk.
42. The audience stood up as she stepped onto the stage.
43. The pharmacy is opposite the school.
44. Wait outside the door.
45. We should lay a blanket over the body.
- past
- per
- plus
- regarding
- round
46. Walk past the museum. The city hall is on your left.
47. We have to pay him €5 per hour.
48. What is ten plus five?
49. Regarding your request, I will reply soon.
50. The Sun goes round the Milky Way.
- save
- since
- than
- through
- throughout
51. The preposition save means 'except for'. All guests arrived on time, save one.
52. I have lived here since 2019.
53. She is taller than her brother.
54. She saw a beautiful cat as she drove through a tunnel.
55. It was raining throughout the night.
- till
- to
- toward
- under
- underneath
56. We have to wait here till noon.
57. Can you give this hat to your sister?
58. She was scared when the stranger walked toward her.
59. Your toy might be under the bed.
60. I found your wallet underneath the car seat.
- unlike
- until
- up
- upon
- versus
61. Unlike his sister, he loves maths.
62. We have to wait until Monday to start the backup.
63. Can she walk up the stairs without help?
64. The decision depends upon funding.
65. Tonight’s match is Spain versus France.
- via
- with
- within
- without
66. Don’t send the file via email. It’s top secret.
67. You can come with your friends if you want.
68. We have to finish within an hour.
69. I can’t work without listening to music.
3.2 Compound preposition list
- according to
- ahead of
- along with
- apart from
1. According to the manual, we need to put this piece here.
2. You should arrive ahead of time for the meeting.
3. She came along with her boyfriend.
4. Apart from Monday, I’ll be available for the rest of the week.
- as for
- as per
- as to
- aside from
5. As for me, I prefer to read a book.
6. As per your message, I will call you tomorrow.
7. As to the new plan, everyone agrees.
8. Aside from her job, she plays the piano.
- because of
- by means of
- close to
- due to
9. We stayed inside because of the rain.
10. The prisoners escaped by means of an underground tunnel.
11. The shop is close to my house.
12. The flight was late due to bad weather.
- except for
- far from
- in addition to
- in accordance with
13. Everyone came except for Tom.
14. Their school is far from here.
15. In addition to English, you will learn Spanish.
16. The rules were changed in accordance with the new law.
- in case of
- in front of
- in light of
- in place of
17. In case of fire, use the stairs.
18. I parked your car in front of the bank.
19. In light of the news, we changed our plans.
20. You can use water in place of milk.
- in connection with
- in spite of
- instead of
- next to
21. The police asked him a few questions in connection with the case.
22. In spite of the rain, they went to the beach.
23. I took the bus instead of driving.
24. Your book is next to mine.
- on account of
- on behalf of
- on top of
- out of
25. The match was cancelled on account of the storm.
26. I’m speaking on behalf of the whole team.
27. Your phone is on top of the table.
28. She ran out of money.
- owing to
- prior to
- in line with
29. Owing to traffic, I arrived late.
30. Prior to the lesson, please read the text.
31. The decision was made in line with the company policy.

4. Positions in sentences
The positions of prepositions in a sentence is important for clarity in English. A preposition usually shows the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other elements in a sentence.
4. 1. At the beginning of a prepositional phrase
Most commonly, prepositions come at the start of a prepositional phrase. A prepositional phrase is a group of words that begins with a preposition and anything that follows it, such as noun, pronoun, or noun phrase.
- She sat on the chair.
- The book is under the table.
Preposition: on
Prepositional phrase: on the chair
Second example:Preposition: under
Prepositional phrase: under the table
In both examples, the preposition on and under is placed at the beginning of the prepositional phrase, followed by the object (the chair and the table). This is the most common position for prepositions.
4.2. In the middle of a sentence
Prepositions can appear in the middle of a sentence. They may come between a verb and its object or between two nouns.
- He went to the park with his friends.
- She put the keys on the desk.
Here, the prepositions to and on link the verb and the location or object.
4.3. At the end of a sentence
In English, prepositions can also appear at the end of a sentence, especially in questions, informal speech, and relative clauses. This is sometimes called a stranded preposition because the preposition is separated from its object.
- What are you looking at?
- This is the book I was telling you about.
Although ending a sentence with a preposition was once considered incorrect, it is now widely accepted in English, especially in spoken and informal contexts.
4.4. Before relative pronouns
Prepositions can be placed before relative pronouns like which, whom, and whose in formal writing. This form is more formal and is typically used in written English.
- The company for which he works is very successful.
- The person to whom you spoke is my manager.
In informal speech, these prepositions can move to the end of the clause, as in: "The company he works for is very successful." This is also correct but less formal.
4.5. In phrasal verbs
Prepositions are also part of phrasal verbs, which combine verbs with prepositions to create new meanings. In phrasal verbs, the preposition typically comes immediately after the verb.
- She looked after her younger brother.
- They ran into an old friend at the store.
Here, looked after and ran into are phrasal verbs where the verb and preposition function as a single unit to convey specific meanings.
