Glossary of internet terms
The internet has its own language. And if you’ve ever read a comment section or overheard teenagers talking, you know it changes fast. Some terms have been around for decades, while others pop up overnight and disappear just as quickly.
In this vocabulary lesson, we will look at both old and new internet terms, from basic technical terms to social media slang that might leave you scratching your head.
1. Internet terms everyone should know these days
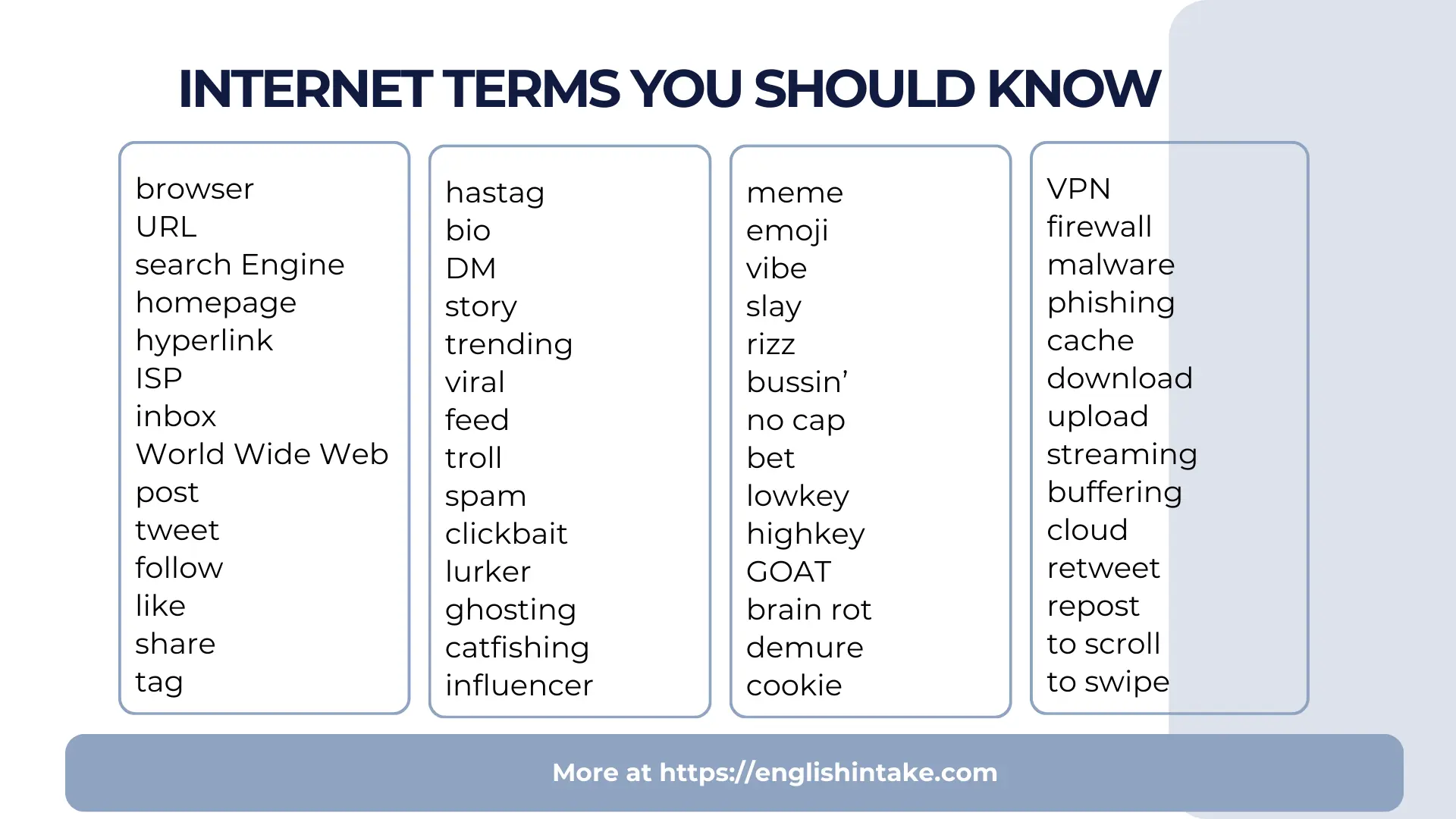
Before getting into the fun stuff, let’s look at the internet terms that have been around since the early days of the World Wide Web.
Browser A browser is a software application that lets you access and view websites on the internet. When you want to visit a website, you open your browser, type in an address or search for something, and the browser fetches that page for you. Common browsers include Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Apple Safari, and Microsoft Edge. Each browser works slightly differently and has its own features, but they all serve the same basic purpose: connecting you to the web. The act of looking through different websites is called browsing or surfing the internet.
URL URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator, which is just a technical way of saying "web address." Every website and webpage has a unique URL that tells your browser exactly where to go. A URL typically starts with "http://" or "https://" followed by the website name, like www.example.com/page. When someone asks for a link, they’re asking for the URL. You can type URLs directly into your browser’s address bar, click on them when they appear as hyperlinks, or copy and paste them from one place to another.
Search engine A search engine is a website or service that helps you find information on the internet. You type in words or questions, and the search engine scans billions of web pages to show you the most relevant results. Google is by far the most popular search engine, handling over 90% of all internet searches worldwide. But alternatives exist, including Bing (owned by Microsoft), DuckDuckGo (which focuses on privacy and doesn’t track your searches), and Yahoo. Search engines use complex algorithms to rank results, trying to show you the most useful and trustworthy pages first.
Homepage A homepage is the main page of a website. It is the first thing you typically see when you visit a site’s primary address. Think of it as the front door or lobby of a building. From the homepage, you can usually navigate to other sections of the website. For example, a news website’s homepage shows the latest headlines, while a company’s homepage might display their products and services. The term can also refer to the page your browser shows when you first open it, which you can customise in your browser settings.
Hyperlink A hyperlink (usually just called a "link") is a clickable element on a webpage that takes you to another location. This could be a different page on the same website, an entirely different website, a specific section of a document, or even a file to download. Hyperlinks can appear as text, images, or buttons. Text hyperlinks were traditionally blue and underlined, which made them easy to spot, but modern web design uses links in all colours and styles. When you hover your mouse over a link, your cursor usually changes to a pointing hand. Links are what make the web a "web". They connect everything together.
ISP ISP stands for Internet Service Provider, which is the company that supplies your internet connection. Without an ISP, you couldn’t get online. ISPs include companies like Comcast, AT&T, Verizon, and countless regional providers. You typically pay them a monthly fee for access, and they provide the infrastructure (cables, fiber optics, or wireless signals) that connects your home or phone to the internet. Different ISPs offer different speeds, prices, and reliability. Your ISP can also see your internet activity, which is why some people use VPNs for privacy.
Inbox In email, your inbox is the folder where all your incoming messages land. When someone sends you an email, it shows up in your inbox until you read it, delete it, or move it somewhere else. Most email services show a number next to your inbox indicating how many unread messages you have. A clean inbox (with zero unread emails) is sometimes called "inbox zero," and some people work hard to maintain it. The word "inbox" has also become a verb in casual online speech. When someone says "inbox me," they’re asking you to send them a private message.
Internet vs. World Wide Web People use these terms interchangeably, but they’re technically different things. The internet is the global network of connected computers and devices—the physical infrastructure of cables, servers, and wireless connections that allows machines to communicate. The World Wide Web (WWW or just "the web") is a service that runs on top of the internet. It’s the system of websites and webpages you access through your browser. Other services also use the internet, like email, video calls, and online gaming. So the internet is like the highway system, while the web is the collection of destinations you can drive to.
2. Social media vocabulary
Social platforms have created their own vocabulary. Here are the words that matter.
Post A post is any piece of content you publish on a social media platform. This could be text, a photo, a video, a link, or a combination of these. When you share something on Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, TikTok, or any other platform, you’re creating a post. Posts can be public (visible to anyone) or private (only visible to certain people). The word works as both a noun ("I saw your post") and a verb ("I’m going to post this photo on Facebook"). Each platform has slightly different names for posts. We say tweets on X, snaps on Snapchat, pins on Pinterest. But post is the term that you can use in all platforms.
Tweet A tweet is a post specifically on X (the platform formerly known as Twitter). Originally, tweets were limited to 140 characters, which forced users to be extremely concise. The limit later expanded to 280 characters, and paid subscribers can now post even longer. "Tweeting" means posting on this platform. The bird logo and bird-related terminology came from the idea of short "chirps" of communication. Even though the platform rebranded to X, many people still use "tweet" and "tweeting" out of habit.
Follow Following someone on social media means subscribing to their account so their posts appear in your feed. When you follow an account, you’ll see their updates without having to visit their profile directly. On platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and X, the terminology is "following" and "followers." On Facebook, the equivalent is "friending" someone, though you can also "follow" pages and public figures without being friends. Following is usually one-directional. You can follow someone without them following you back. Your "follower count" refers to how many people follow you.
Like A like is a quick way to show appreciation for someone’s content. Almost every social platform has some version of this in the form of a heart, a thumbs up, or another symbol you click or tap to indicate you enjoyed something. On Instagram, you can double-tap a photo to like it. Likes are visible to others and often displayed as a count beneath posts. Some platforms have expanded beyond simple likes to include other reactions (like Facebook’s love, laugh, sad, and angry buttons). For content creators and businesses, likes are an important metric that shows engagement.
Tag Tagging is the act of linking someone’s profile to a post, photo, comment, or location. When you tag someone in a photo, their username becomes a clickable link, and they usually receive a notification. This connects the content to their profile and often makes it visible to their followers too. You can tag people in captions, comments, or directly on images (like identifying who’s in a group photo). Tagging is also used for locations.
Hashtag A hashtag is a word or phrase preceded by the # symbol, like #MondayMotivation or #ThrowbackThursday. Hashtags were originally created on Twitter as a way to categorise and search for related content. If you click on a hashtag, you’ll see other posts using the same tag. This makes them useful for following events, topics, or trends. But hashtags have evolved beyond their original purpose. People use them these days for humour, emphasis, or commentary at the end of their posts. Using too many hashtags looks spammy, but strategic use can help content get discovered.
Bio Your bio is the short description that appears on your social media profile. It’s usually limited to a certain number of characters (160 on X, 150 on Instagram) and serves as a quick introduction to who you are. Bios typically include your name, what you do, your interests, and sometimes a link to your website or other content. Since it’s one of the first things people see when visiting your profile, a good bio makes a strong impression. Some people keep bios straightforward and professional, while others use them for humour or self-expression.
DM (Direct Message) A DM is a private message sent between users on a social platform. Unlike posts that anyone can see, DMs are only visible to the sender and recipient. Most platforms have built-in messaging features where you can have one-on-one or group conversations. "Sliding into someone’s DMs" has become slang for sending someone a private message, often with romantic intent. DMs are used for personal conversations, customer service inquiries, business collaborations, and everything in between.
Story A story is a type of content that disappears after 24 hours. Snapchat invented this format, but Instagram copied it successfully, and now Facebook, LinkedIn, and other platforms have stories too. Stories appear at the top of your feed in circular icons, and you tap through them rather than scrolling. Because they’re temporary, stories feel more casual and spontaneous than permanent posts. People use them to share daily moments, behind-the-scenes content, polls, questions, and time-sensitive updates. Some stories can be saved as "highlights" on your profile.
Trending Something is trending when it’s currently extremely popular and being discussed widely across a platform. Most social networks have a "trending" section that shows the most talked-about topics, hashtags, or content at any given moment. Trending topics change quickly and often reflect breaking news, viral moments, cultural events, or internet phenomena. Getting a post to trend or being associated with a trending topic can dramatically increase visibility. The specific trending topics you see may vary based on your location and interests.
Viral Content goes viral when it spreads rapidly across the internet, reaching a massive audience in a short time. Viral posts get shared, reshared, and discussed by millions of people, far beyond the original creator’s network. Going viral isn’t something you can easily plan or predict. It usually requires content that resonates emotionally, surprises people, or feels extremely timely. Viral content can make unknown people famous overnight, launch products, or shape public conversations. The term comes from how viruses spread from person to person.
Feed Your feed (also called newsfeed or timeline) is the stream of content you see when you open a social media app or website. It displays posts from accounts you follow, ads, suggested content, and other updates. Feeds are typically sorted by algorithms that try to show you what you’re most likely to engage with, though some platforms let you switch to a chronological view. "Scrolling through your feed" is how most people consume social media. The feed is personalised to each user based on their follows, interests, and behaviour.
3. Words that describe online behaviour
The internet has not only created new words for technology, but also words describing how people act online.
Troll A troll is someone who deliberately posts inflammatory, offensive, or provocative content online with the intention of upsetting others. Troll is also a verb that means to annoy someone by posting offensive message on the internet. Trolls doesn’t necessarily reflect the views of the person who posted them. Many people troll in order to get social media reactions. They might post outrageous statements in comment sections, argue in bad faith, or harass specific users. Trolling is the act of behaving this way, and "Don’t feed the trolls" is common advice meaning you shouldn’t engage with them because your attention is what they want. Trolling ranges from mildly annoying to seriously harmful.
Spam Spam refers to unwanted, unsolicited messages sent in bulk, usually for advertising, scams, or spreading malware. The term originally applied to junk email, e.g., emails about lottery winnings or offers for products you never wanted. But spam now appears everywhere: in comment sections, social media DMs, text messages, and more. Email services have spam filters that automatically detect and redirect these messages to a junk folder. Sending spam is called "spamming," and people who do it are "spammers." The term reportedly comes from a Monty Python sketch where the word "spam" is repeated annoyingly.
Clickbait Clickbait is content with a sensationalised, misleading, or curiosity-provoking headline designed to get you to click. Classic clickbait uses phrases like "You won’t believe what happened next," "This one weird trick," or "Number 7 will shock you." The actual content rarely lives up to the headline’s promise. Clickbait works because it exploits curiosity, but it frustrates users when the payoff doesn’t match the hype. While clickbait can generate lots of clicks in the short term, it often damages trust. Websites that rely heavily on clickbait are generally considered low-quality.
Lurker A lurker is someone who reads, watches, and follows online discussions without actively participating in them. They consume content in forums, comment sections, social media, and online communities but rarely or never post, comment, or otherwise make their presence known. Lurking isn’t necessarily negative. Many people prefer to observe something rather than to participate in it, especially when they’re new to a community. Some lurkers eventually become active contributors. The term comes from the idea of someone "lurking in the shadows" and watching without being seen.
Ghost/Ghosting Ghosting means suddenly cutting off all communication with someone without any explanation. One day you’re having conversations; the next day, you cut yourself off from any forms of communication. The term originated in dating contexts (when someone you’ve been seeing suddenly disappears) but now applies to any online or real-life relationship. Getting ghosted can be confusing and hurtful because there’s no closure. People ghost for various reasons: they’re conflict-avoidant, they’ve lost interest, or they simply don’t know what to say.
Catfishing Catfishing is the act of creating a fake online identity to deceive or manipulate someone, usually for romantic or financial purposes. A catfish might use stolen photos, invent a false backstory, and develop relationships with victims who believe they’re talking to a real person. The deception can continue for weeks, months, or even years. The term became popular after the 2010 documentary "Catfish" and the subsequent TV show where hosts help people investigate whether their online relationships are real. Catfishing is emotionally damaging and sometimes illegal.
Influencer An influencer is someone with many people following them on social media. Influencers can affect the opinions and purchasing decisions of their audience. They create content around specific niches (fashion, fitness, gaming, travel, parenting, cooking, and countless others). Brands pay influencers to promote products to their followers, which has turned influencing into a career for many people. Influencer counts range from "nano-influencers" with a few thousand followers to mega-influencers with millions. The key is the ability to influence (hence the name).
4. Internet slang that’s been sticking around
The following slang terms have survived for a long time.
Meme A meme is an image, video, phrase, or concept that spreads rapidly across the internet, usually in modified forms. Memes typically follow a recognisable format (a specific image with text, a style of video, or a type of joke) that people adapt with their own variations. The "distracted boyfriend" photo, "woman yelling at cat," and countless others are meme formats that have been reused millions of times with different captions. Memes reflect internet culture and often serve as commentary on current events, relatable experiences, or absurd humour. They spread because people enjoy creating their own versions and sharing them.
Emoji Emojis are small digital images or icons used to express emotions, ideas, or objects in electronic communication. They evolved from simple text emoticons like :) and :( into a standardised set of colourful images. Today there are thousands of emojis covering facial expressions (😊 😂 😢), gestures (👍 👋), objects (📱 🚗), food (🍕 🍔), animals (🐱 🐕), and much more. Emojis add tone and personality to text-based communication. They help you express feelings that words alone cannot. Different platforms display emojis slightly differently, but they’re universally recognised.
Vibe In internet slang, a vibe refers to the overall feeling, atmosphere, or energy of something. It can describe a place ("this café has good vibes"), a person ("she gives off positive vibes"), content ("this playlist has chill vibes"), or almost anything else. "Vibe check" means assessing someone’s mood or the atmosphere of a situation. The word has been around for decades but became much more popular through social media. "Vibing" means relaxing or enjoying yourself, and "vibes" can be good, bad, weird, immaculate, or anything in between.
Slay To slay means to do something exceptionally well, to look amazing, or to succeed impressively. When someone says "you slayed that presentation" or "she’s slaying in that outfit," they’re offering high praise. The term has roots in drag and ballroom culture, where it was used to compliment someone’s appearance or performance. It spread to mainstream internet culture through social media and pop culture. "Slay" is always positive and enthusiastic. it’s the kind of compliment you give when someone exceeds expectations.
Rizz Rizz is short for charisma, specifically the ability to attract romantic interest through charm, confidence, and smooth conversation. Someone with "rizz" is naturally good at flirting and making romantic connections. The term was popularised by YouTuber and streamer Kai Cenat and went mainstream around 2023, becoming Oxford’s Word of the Year. You can have "W rizz" (good/winning rizz) or "L rizz" (bad/losing rizz). "Rizzing someone up" means successfully charming them. It’s used mostly among younger generations to describe dating and social skills.
Bussin’ Something that’s bussin’ is really, really good. The term is most commonly used for food—when a meal is exceptionally delicious, it’s bussin’. But it can apply to anything that’s impressive, enjoyable, or high-quality. "These tacos are bussin’" or "That new album is bussin’" both work. For extra emphasis, people sometimes say something is "bussin’ bussin’" (repeating it twice). The term originated in African American Vernacular English (AAVE) and spread widely through social media, especially TikTok.
No cap "No cap" means "no lie" or "I’m being completely serious." It’s used to emphasise that what you’re saying is true and not exaggerated. "That film was the best I’ve ever seen, no cap." The opposite is "cap" or "capping," which means lying or exaggerating. "You’re capping" means "you’re lying." The origin isn’t entirely clear, but "cap" meaning a lie has been part of slang since at least the early 1900s, and the phrase became popular on social media around 2018-2019.
Bet "Bet" is a quick way to say "okay," "sounds good," "agreed," or "I’m in." It’s an expression of confirmation or approval. If someone asks "Want to grab dinner at 7?" responding with "Bet" means yes, you’re confirming the plan. It’s casual and efficient. This term has evolved from expressions like "you bet" and has been used in various communities for decades, but social media spread it to wider use.
Lowkey/Highkey Lowkey means somewhat, kind of, or secretly. It indicates that something is true but understated or not widely known. "I lowkey love that song" means you like it more than you’d openly admit. Highkey is the opposite of lowkey. It means obviously, openly, or very much. "I highkey need a vacation" means you really, desperately need time off and you don’t care who knows it. These terms add nuance to statements, indicating the degree to which something is true or how openly you’re expressing it.
GOAT GOAT stands for "Greatest Of All Time" and is used to describe someone who’s the absolute best at what they do. Athletes often get this endless debate about who’s the GOAT of basketball or football. But it applies beyond sports too. Someone might call their grandmother the GOAT of cooking or say a certain album is the GOAT. It’s the highest possible praise, reserving the title for only the most exceptional.
Brain rot Brain rot refers to mindless, low-quality internet content or the mental effects of consuming too much of it. Spending hours scrolling through repetitive videos, absurd memes, and shallow content might give you "brain rot." The term also describes content itself that’s considered vapid or meaningless. It became especially popular in 2024, with Oxford naming it a Word of the Year.
Demure While "demure" is actually an old English word meaning modest and reserved, it went viral in 2024 after content creator Jools Lebron used it in TikTok videos describing understated, mindful behaviour. Being "very demure, very mindful" became a meme and catchphrase. The internet resurrected this word and gave it new life as a way to describe someone who’s calm, classy, and not trying too hard to get attention. It’s often used humourously.
5. Technical terms that is widely used
You don’t need to be a programmer to encounter these words regularly.
Cookie In web terms, a cookie is a small piece of data that a website stores on your computer or device. Cookies remember information about you (your login status, shopping cart contents, preferences, and browsing history). When you return to a website and it remembers your settings or keeps you logged in, that’s cookies working. Some cookies are essential for websites to function, while others track your behaviour for advertising purposes. Privacy concerns around tracking cookies have led to laws requiring websites to ask for consent before using certain types of cookies.
VPN (Virtual Private Network) A VPN is a service that creates a secure, encrypted connection between your device and the internet. When you use a VPN, your internet traffic is routed through the VPN provider’s servers, which masks your actual IP address and location. This provides privacy by making it harder for websites, advertisers, and even your ISP to track your online activities. VPNs allow you to access internet content that’s been blocked in your regions.
Firewall A firewall is security software or hardware that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic. It acts as a barrier between your device or network and the broader internet, blocking potentially harmful connections while allowing safe ones. Firewalls use predefined rules to determine what traffic is acceptable. Your computer likely has a built-in firewall, and businesses use more sophisticated ones to protect their networks. The term comes from physical firewalls (walls designed to prevent the spread of fire in buildings).
Malware Malware is short for "malicious software". It refers to any computer program designed to harm, exploit, or otherwise compromise your device. Viruses, ransomware, spyware, trojans, and worms are all types of malware. Malware can steal your personal information, lock your files until you pay a ransom, damage your system, or use your computer for illegal activities. It spreads through infected downloads, malicious email attachments, compromised websites, and other vectors. Antivirus software helps detect and remove malware.
Phishing Phishing is a type of scam where attackers try to trick you into revealing sensitive information like passwords, credit card numbers, or personal details. Phishing attempts often come as emails, text messages, or fake websites that impersonate legitimate companies. A phishing email might look like it’s from your bank, asking you to "verify your account" by clicking a link that leads to a fake login page. The term is a play on "fishing" because the scammers are literally fishing for victims. Learning to recognise phishing attempts is an important internet safety skill.
Cache A cache (pronounced "cash") is temporary storage that saves copies of data so it can be accessed faster later. Your browser caches elements of the websites you visit (images, scripts, and other files) so that pages can load more quickly when you return to access them. If a website seems stuck showing old content, "clearing your cache" forces the browser to download fresh copies of everything. Caches exist throughout technology, from your browser to your phone to complex server systems. They speed things up but sometimes cause issues when outdated data needs to be refreshed.
Download/Upload Downloading means transferring files from the internet to your device. When you download a film, app, document, or any file, you’re copying it from a remote server to your local storage. Uploading is the opposite of downloading. When you upload something, you are sending files from your device to the internet. When you upload a photo to social media or attach a document to an email, you’re transferring data from your device to someone else’s server. Download and upload speeds (measured in Mbps) indicate how fast you can transfer data in each direction.
Streaming Streaming is a method of consuming media where content is played in real-time as it’s delivered over the internet, rather than downloading it first. When you watch Netflix, listen to Spotify, or view a live broadcast, you’re streaming. The data comes in continuously, allowing you to start watching or listening immediately rather than waiting for a complete download. Streaming requires a stable internet connection; if your connection drops, the content buffers (pauses while it loads more data). Streaming services have largely replaced traditional downloading for films, music, and TV shows.
Buffering Buffering is the pause that occurs when streaming content can’t load fast enough to play smoothly. You’ll see a loading icon (often a spinning circle) while your device waits for more data to arrive. Buffering happens when your internet connection is slower than the rate at which you’re consuming content, or when the server is struggling to deliver data quickly enough. Better internet connections and lower-quality video settings reduce buffering. It’s one of the most common frustrations of streaming media.
Cloud "The cloud" refers to remote servers that store and process data, accessible from anywhere via the internet. When you save files to the cloud (using services like Google Drive, Dropbox, or iCloud), they’re stored on servers in data centres around the world rather than just on your local device. Cloud computing allows you to access your files, photos, and applications from any device with an internet connection. It also enables services to scale their computing power without owning physical hardware. Despite the ethereal name, the cloud is just other people’s computers in warehouses.
Algorithm An algorithm is a set of rules or instructions that a computer follows to solve a problem or perform a task. In social media and internet contexts, "the algorithm" usually refers to the complex systems that decide what content you see. Social platforms use algorithms to analyse your behaviour (what you like, share, comment on, and how long you spend viewing different content—to predict what you’ll engage with next). "Fighting the algorithm" or "getting picked up by the algorithm" are phrases you might encounter online. These systems aren’t transparent, so users usually guess at how they work.
6. Platform-specific terms
Different platforms have their own vocabulary. Each social network and online service has developed its own terminology based on its unique features and culture.
Retweet/Repost A retweet is when you share someone else’s tweet to your own followers on X (formerly Twitter). The original post appears on your timeline with attribution to the original author. You can retweet silently or add your own comment (a "quote tweet"). "Repost" is used similarly on other platforms like Instagram, where you might repost someone’s story or use third-party apps to reshare posts. Retweeting and reposting help content reach wider audiences and are key to how things go viral.
Snap A snap is a photo or video sent through Snapchat. What makes snaps unique is their ephemeral nature; they disappear after being viewed (unless the recipient takes a screenshot, which notifies the sender). You can add filters, stickers, drawings, and text to snaps before sending them. Snaps can be sent directly to individuals or added to your "story" for all friends to see. The temporary format encourages sharing more casual, in-the-moment content since it won’t stick around permanently.
Reel A reel is a short-form video on Instagram, similar to TikTok videos. Reels can be up to 90 seconds long and typically feature music, effects, and creative editing. They appear in a dedicated Reels tab and are prominently featured in Instagram’s algorithm because they drive high engagement. Creating reels has become essential for content creators and businesses trying to grow on Instagram. The format emphasises entertainment, trends, and quick, attention-grabbing content.
Subreddit A subreddit is a community within Reddit focused on a specific topic. Each subreddit has its own name (preceded by "r/"), rules, culture, and moderators. There are subreddits for virtually every interest imaginable—from r/science and r/news to r/cats and r/mildlyinteresting. Users "subscribe" to subreddits they’re interested in, and posts from those communities appear in their home feed. Subreddits can range from a few hundred members to tens of millions, each functioning as its own discussion board.
Thread A thread is a connected series of posts or messages forming a single conversation. On X, a thread is multiple tweets from the same user, posted in sequence to extend beyond the character limit. On Reddit and forums, a thread starts with an original post and includes all the comments and replies beneath it. Email threads show the back-and-forth of a conversation. Threads keep related content organised and make it easier to follow discussions over time.
AMA (Ask Me Anything) An AMA is a question-and-answer session where someone (often a celebrity, expert, or interesting person) invites the public to ask them anything. AMAs originated on Reddit’s r/IAmA subreddit and have featured everyone from Barack Obama to astronauts to random people with unusual jobs. The format has spread to other platforms like Instagram and X, where people host AMAs in their stories or posts. AMAs are valued for their directness and the opportunity to ask questions you’d never normally get answered.
Live stream A live stream is video content broadcast in real-time over the internet. Unlike pre-recorded videos, live streams happen as you watch them, creating a sense of immediacy and interaction. Viewers can often comment or react during live streams, and the streamer can respond. Platforms like Twitch, YouTube Live, Instagram Live, and Facebook Live have made live streaming accessible to anyone. Content ranges from gaming and music performances to tutorials, Q&As, and just chatting. Live streaming has become a major form of entertainment and a career for many creators.
Podcast A podcast is an audio program available as a series of episodes that you can download or stream. Podcasts cover many topics (news, comedy, true crime, interviews, education, storytelling, and more). They’re typically free and accessible through apps like Spotify, Apple Podcasts, or dedicated podcast players. Unlike radio, podcasts are on-demand, so you listen when you want. Episodes range from a few minutes to several hours, and many podcasts release new episodes weekly. The term comes from combining "iPod" and "broadcast."
Blog A blog is a website or section of a website that contains regularly updated content, usually written in a conversational style. Short for "web log," blogs originally served as personal online journals where people wrote about their lives. They’ve evolved to include professional publications, company updates, tutorials, reviews, and every other type of written content. Someone who writes a blog is a "blogger," and the act of writing blog posts is "blogging." Blogs helped democratise publishing because anyone with an internet connection could become a writer with a potentially global audience.
7. Verbs the internet has created
The internet has turned many nouns into verbs that we end up using every day.
To Google To search for something online, typically using the Google search engine. "Just Google it" has become universal advice for finding information. The verb is so common that it’s been added to major dictionaries, though Google the company has mixed feelings about its trademark becoming generic. You might "Google" on Bing and no one is going to correct your word choice. This verb has transcended its origin.
To stream To watch or listen to content online as it’s delivered in real-time, rather than downloading it first. "I streamed the whole series last night" or "I’ll stream some music while I work." Streaming has largely replaced downloading for entertainment consumption, and the verb reflects this shift in how we access media.
To scroll To move through content on a screen, typically by swiping your finger on a touchscreen or using a mouse wheel. We "scroll through" our feeds, articles, and apps. "Doomscrolling" is the phenomenon of compulsively scrolling through bad news. The physical action has become so associated with browsing content that the verb now implies consuming information, not just moving through it.
To swipe To make a sweeping gesture across a touchscreen with your finger. On dating apps like Tinder, swiping right indicates interest in someone while swiping left indicates rejection. This gesture has become so iconic that "swipe right" is used metaphorically to mean approval or selection. "I’d swipe right on that job opportunity."
To unfollow/unsubscribe To stop receiving updates from an account or mailing list. Unfollowing someone on social media removes their posts from your feed. Unsubscribing from emails should (legally) remove you from a mailing list. These actions are ways of curating what content you see and what you don’t want cluttering your digital life.
To block To prevent someone from contacting you or viewing your content on a platform. When you block someone, they typically can’t see your profile, send you messages, or interact with you in any way. Blocking is more severe than unfollowing. It’s a complete cut-off used for harassment, unwanted attention, or just people you don’t want in your digital space.
8. Other words that you should be familiar with
Engagement Engagement refers to all the ways people interact with online content—likes, comments, shares, clicks, views, saves, and any other measurable action. High engagement means lots of people are actively responding to content, not just passively viewing it. For content creators and businesses, engagement rates are key performance indicators. Algorithms tend to favour content with high engagement, showing it to more people.
Content creator A content creator is anyone who produces material for digital platforms (videos, articles, photos, podcasts, music, art, or any other type of content). The term encompasses professional YouTubers, TikTok influencers, bloggers, podcasters, and anyone who regularly creates and shares content online. "Creator" has become a preferred term over "influencer" for many, as it emphasises the creative work rather than just the audience size.
Handle Your handle is your username on a social platform, particularly on X. Handles start with the @ symbol (like @username) and are how people tag or mention you. Choosing a good handle is important for personal branding since it’s often how people find and identify you. Some people use their real name; others create memorable pseudonyms.
Avatar An avatar is the image that represents you online, typically your profile picture. It could be a photo of yourself, a cartoon representation, a logo, or any image you choose. The term comes from Hindu mythology (where an avatar is a deity’s earthly incarnation) and was adopted by early internet culture. In gaming and virtual worlds, avatars can be fully customizable digital characters you control.
UGC (User-Generated Content) UGC refers to any content created by regular users rather than companies, brands, or professional creators. Reviews, social media posts, videos, photos, and forum discussions are all UGC. Brands often encourage UGC because it serves as authentic endorsements. When companies repost customer photos or testimonials, that’s leveraging UGC for marketing.
9. The bottom line
Internet vocabulary keeps evolving. Some of these terms will stick around for years, while others might feel outdated by next month. The best way to stay up-to-date is to pay attention to how people communicate online. If you come across a word you don’t recognise, google it. That’s what search engines are for.
