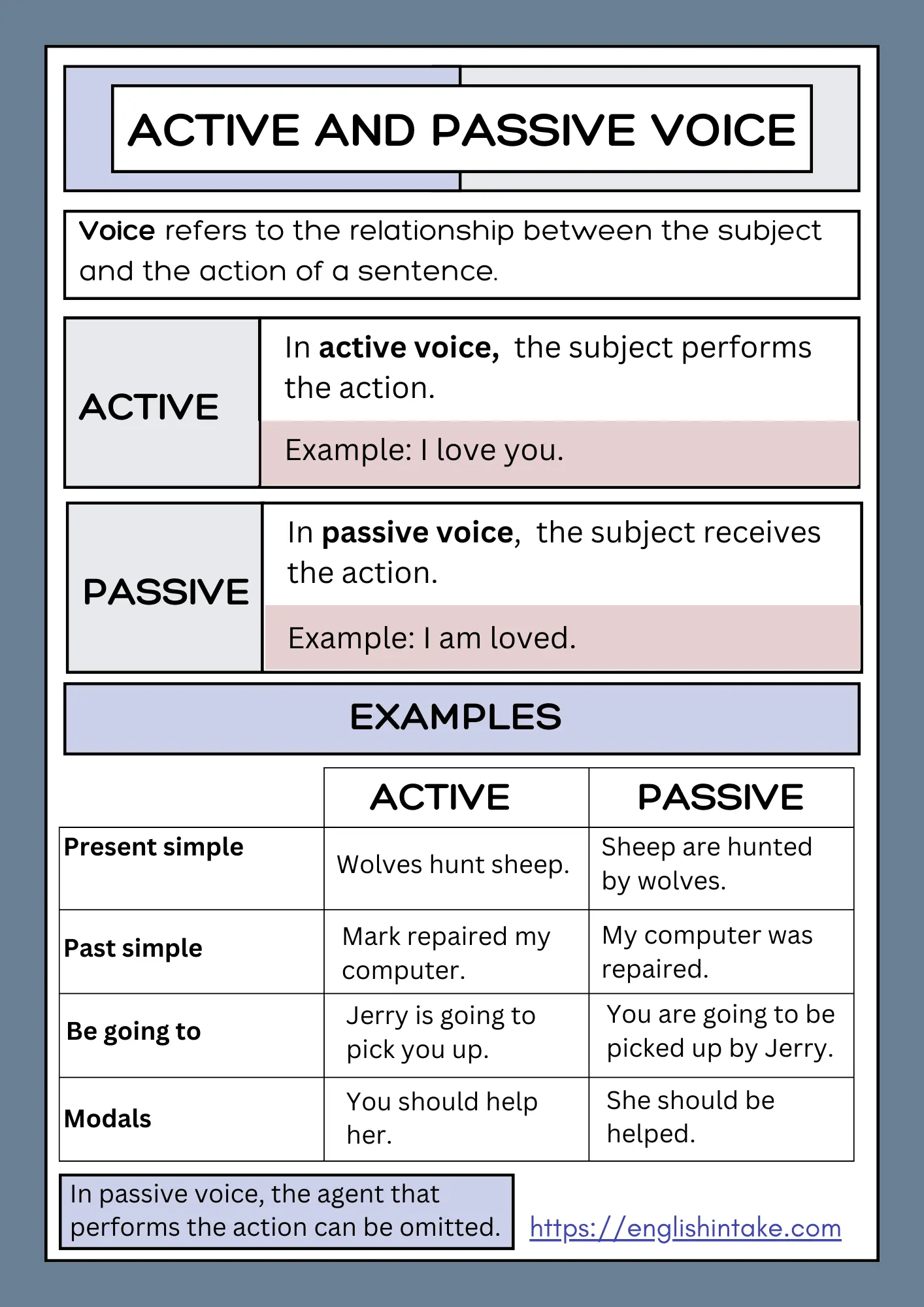
1. Active and passive voice
Active and passive voice represent two grammar structures that show whether the subject does the action or receives the action in a sentence.
The table below summarises the difference between these two voices.
| Voice | Note | Example | When to use it |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active |
|
William painted the wall. |
|
| Passive |
|
The wall was painted by William. |
|
2. Difference
In active voice, the subject comes first, followed by the verb and the object.
- I love you.
- He needs her.
- Donald built this house in 1999.
- The police killed the suspect.
A sentence in passive voice uses a conjugated form of to be followed by a past participle.
It follows the structure: object + 'be' verb + past participle + (by + subject).
Study the examples below.
- The suspect was killed by the police.
- This house was built by Donald in 1999.
- This grammar lesson was written by ESL teachers.
3. Forms
The gardener mows the lawn every week.
The lawn is mowed by the gardener every week.
The gardener is mowing the lawn.
The lawn is being mowed by the gardener.
Robert painted the wall.
The wall was painted by Robert.
A contractor was building the house.
The house was being built by a contractor.
The courier will deliver the package tomorrow.
The package will be delivered by the courier tomorrow.
The courier is going to deliver the package tomorrow.
The package is going to be delivered by the courier tomorrow.
The courier has delivered the package.
The package has been delivered by the courier.
A contractor had constructed the building.
The building had been constructed by a contractor.
The chef will have baked the cake by the time the party starts.
The cake will have been baked by the chef by the time the party starts.
You should repair the fridge.
The fridge should be repaired.