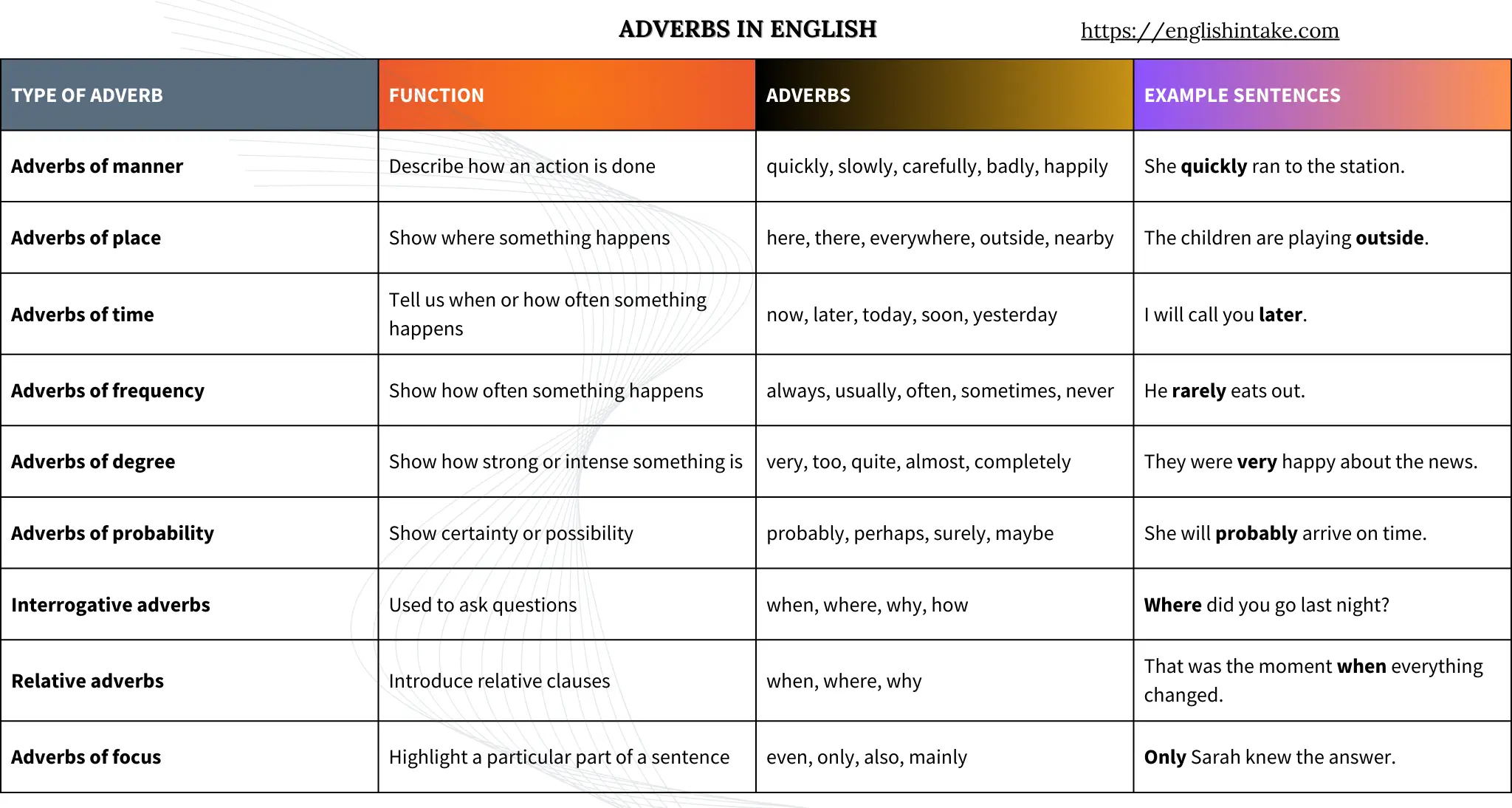
Using adverbs in sentences adds details and clarity to your message. They help explain how, when, where, or how often an action happens. For example:
- She speaks clearly.
1. What are adverbs?
Adverbs add more information about a verb, an adjective, another adverb, or even an entire sentence. They tell us:
- How something happens (He runs quickly.)
- When it happens (She arrived yesterday.)
- Where it happens (They live nearby.)
- How often it happens (I always wake up early.)
- To what extent or how much (She was very tired.)
They can also modify a whole sentence to the speaker’s attitude or opinion. For example:
- Obviously, she was upset.
- Fortunately, we arrived on time.
2. Places of adverbs in sentences
An adverb can be placed in various positions in a sentence. However, It’s important to note that there are many variations and exceptions to adverb placement depending on the context and the intended meaning of the sentence. Study the examples below.
- She only gave me two dollars.
Here the emphasis is on the verb give. In other words, the adverb only modifies the verb give. In this sentence, the adverb only emphasises the limitation or restriction of what was given. The sentence could mean that the speaker expected:
- two dollars and something else,
- an amount of money more than two dollars,
- or something other than the two dollars given. The donor might have wanted to give something more but couldn’t do so due to some constraints.
Now, let’s change the position of the adverb:
- She gave me only two dollars.
Here, the focus is on the amount given, which is two dollars. The adverb "only" emphasises how insignificant the amount is. The sentence suggests that the donor intentionally chose to give only two dollars, and may not have intended or wanted to give more.
2.1 Before verbs
I quickly rushed to the hospital as soon as I heard that my friend was involved in a car accident.
The traffic is moving very slowly today.
She clearly explained the rules to the new students.
She confidently defended her thesis at the University of Cambridge last week.
The mother fiercely defended her children from criticism.
He honestly admitted his mistake and apologised.
A careless driver nearly knocked me over this morning.
I absolutely love spending time with my family.
I usually go to bed around 11 PM.
I definitely need more training before my next competition.
She intentionally ignored his calls.
2.2 Before adjectives
She was very happy to hear the good news.
The food was quite delicious.
The injury was incredibly painful.
The weather was extremely hot.
The test was fairly difficult.
The movie was somewhat boring.
I am really excited to start my new job.
The coffee was slightly bitter.
The experiment went terribly wrong.
That was pretty cool.
The news was utterly shocking.
2.3 Describing other adverbs
The traffic is moving very slowly today.
I’m almost always on time for work.
He was speaking too loudly in the library.
I was able to fix the computer surprisingly easily.
He finished the project rather quickly.
Your hair is so nicely combed.
My phone is almost fully charged.
She did her exam exceptionally well.
2.4 Describing sentences
Surprisingly, she finished the marathon in less than three hours.
Regrettably, I won’t be able to join you for dinner tonight.
Interestingly, the study found no correlation between diet and cancer risk.
Obviously, the driver didn’t see the stop sign.
Eventually, we reached our destination on time.
Honestly, I don’t think she is ready for her exam.
She will pass her exam, undoubtedly.
My father won’t be at my wedding day, unfortunately.
3. Prepositions vs adverbs in sentences
There are several words in English that can function both as prepositions and adverbs depending on how they are used in a sentence. Study the following examples:
| Word | As a preposition | As an adverb |
|---|---|---|
| Up | She walked up the stairs. (Up shows the relationship between "walked" and "stairs".) | She looked up at the sky. (Up modifies the verb "looked" by describing the direction of her gaze.) |
| Over | The plane flew over the mountains. (Over shows the relationship between "flew" and "mountains".) | An aeroplane flew over while we were playing in the garden. (Over modifies the verb "flew" by describing the movement of the airplane.) |
| Around | We walked around the city. (Around shows the relationship between "walked" and "city".) | She looked around nervously. (Around modifies the verb "looked" by describing the manner in which she looked.) |
| Through | He walked through the park. (Through shows the relationship between "walked" and "park".) | I read the entire book through in one sitting. (Through modifies the verb "read" by describing the manner in which I read the book.) |
| Across | The cat walked across the street. (Across shows the relationship between "walked" and "street".) | He threw the ball across, and it landed perfectly in his friend's hands. (Across modifies the verb "threw" to show the direction in which the ball was thrown.) |
| Opposite | The Chinese restaurant is opposite the train station. (Opposite shows the location of the Chinese restaurant with respect to the train station.) | The Chinese restaurant is over there, just opposite. (Opposite provides additional information about the location of the Chinese restaurant.) |
Distinguishing between a preposition and an adverb can sometimes be tricky, but there are some clues to look for in a sentence that can help you identify which one is being used:
1. Prepositions usually come before a noun or pronoun and show the relationship between that noun or pronoun and other words in the sentence.
2. Adverbs, on the other hand, typically modify sentences, verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, and can provide information about how, when, where, why, or to what extent an action is performed.
4. Adverbs vs adjectives
Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns or pronouns. They provide details about an object’s characteristics, such as size, shape, age, colour, or origin.
- It’s a beautiful day.
- He’s a tall man.
- They live in a big house.
- He is always calm and relaxed.
Adverbs, on the other hand, are words that describe or modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They provide information about how, when, where, why, or to what degree something happens.
- He runs quickly. (how)
- I went to the dentist yesterday. (when)
- He lives nearby. (where)
- She totally agrees with you. (to what degree)
5. Using different types of adverbs in sentences
Some adverbs may belong to multiple types depending on their usage and context. Study the examples below.
That was well worth the effort. (Indicating a high degree of value or worth.)
She sings well. (Describing how the action is performed.)
I certainly did not expect to see you here! (Emphasising surprise.)
I certainly agree with you on that point. (Affirming your level of agreement.)
5.1 Time
At the present moment; immediately.
I don't want to go out now.
During the course of the present day; on the present day.
I am meeting with a client later today.
During the course of this night; on the present night.
I am planning to watch a movie tonight.
The day before today; in the recent past.
I ran across my childhood friend yesterday.
The day after today.
I have a meeting scheduled for tomorrow morning.
At a subsequent time; after a while.
I will respond to your email later today.
Before the expected or planned time; near the start of a period of time.
I woke up early to go for a run.
At a time preceding the present time; previously.
We wouldn't have this problem if we had acted earlier.
After the expected or usual time; behind schedule.
He arrived late yesterday.
In the near future; shortly.
I will be traveling to Europe soon.
At the present time; currently.
She is presently working on a new project.
At the present time; right now.
I am currently reading a book.
At an earlier time; before the present time.
I had previously worked for a different company.
After a particular event or time; later on.
Lucy lost her job unexpectedly and subsequently struggled to pay her bills for several months.
At a later time; following an event.
They were enemies before the election but became friends afterwards.
At that time; next in order of time.
First, we will finish this project, then we can move on to the next one.
At an earlier time; prior to the present time.
I had to finish my homework before I could watch TV.
Subsequent to a particular event or time.
We went out for lunch after the meeting.
At the same time as; throughout the duration of an event or period.
I listen to music during my commute to work.
In the meantime; while waiting for a certain event to occur, or during the occurrence of another event.
Lucy is saving money to buy a new car. Meanwhile, she is using public transportation to get around.
From a particular time in the past until now.
I have been working here since 2010.
Before the present time; previously.
I have already eaten breakfast this morning.
At any time up to the present moment; still.
I haven't finished my work yet.
A moment ago; very recently.
I just finished my lunch.
At a recent time; not long ago.
I recently moved to a new city.
In the recent past; recently.
I have been studying a lot lately.
At a time far in the past; a considerable time ago.
I visited that city a long time ago.
At some time in the future; ultimately.
She will eventually break up with him if he doesn't change his habits.
Before anything else in order, time, or importance.
He came first in the race.
Up to and including the present or the time mentioned; yet.
I am still waiting for my friend to arrive.
Coming immediately after the present time, order, or position.
Who wants to go next?
At the end of a period of time or a series of events.
Finally, we arrived at our destination after a long journey.
5.2 Frequency
At all times; on all occasions.
I always brush my teeth before going to bed.
In the way or manner most commonly occurring.
I usually have a cup of coffee in the morning.
Frequently; many times.
I often go to the gym after work.
At frequent intervals; often.
I frequently visit my grandmother in the nursing home.
On certain occasions or in certain circumstances, but not always.
Sometimes I have trouble falling asleep at night.
At infrequent or irregular intervals; from time to time.
I occasionally drink alcohol.
Not often; rarely.
I seldom go to the cinema because I prefer reading.
Not often; seldom.
I rarely eat fast food to stay healthy.
Almost never; very rarely.
I hardly ever go out on weekdays because I have to work.
Virtually never; almost not at all.
I almost never drink alcohol.
Not at any moment or not on any occasion.
I never skip breakfast because it’s the most important meal of the day.
At any time.
Have you ever been to Paris?
Happening every day.
I take a walk in the park daily.
Happening every week.
I plan to have our first weekly meeting this Thursday.
Happening every month.
I pay my rent monthly.
Happening every year.
The company holds a party annually in December.
Happening twice a year.
The newsletter is published biannually in June and December.
Happening every hour.
The train departs hourly from the station.
Happening at fixed intervals or with consistency.
I exercise regularly to stay healthy.
Happening in the same way over time; without variation.
He consistently performs well at his job.
Happening from time to time; not regularly.
The wifi signal is intermittently weak in this area.
Happening occasionally or in isolated instances.
I only see my old friends sporadically since they live far away.
Happening at regular intervals.
The car needs to be serviced periodically to maintain its performance.
Happening rarely or not very often.
Snow falls infrequently in the southern part of the country.
Happening without interruption or cessation.
She is constantly checking her phone for messages.
Happening without interruption or pause.
The rain has been falling continuously for two hours.
Doing something by habit or on a regular basis.
He habitually goes for a run every morning before work.
Doing something as part of a regular procedure or habit.
She routinely checks her email first thing in the morning.
Happening occasionally; not very often.
I only go to the cinema once in a while.
Happening occasionally; at intervals.
He visits his hometown from time to time.
5.3 Manner
In a sudden and unexpected way.
He left the room abruptly without saying goodbye.
With great attention, care, or concern.
She handled the fragile vase carefully to avoid breaking it.
In a cheerful or happy manner.
The children played cheerfully in the park on a sunny day.
In a clear or distinct manner.
She spoke clearly so that everyone could understand her message.
In a way that is physically close or with close attention.
The police are watching the suspect closely.
In a careful and intentional way.
He was killed deliberately.
In a way that shows enthusiasm or eagerness.
The children waited eagerly for their presents on Christmas morning.
In a stylish manner; gracefully.
She walked elegantly in her long gown at the ball.
In a way that shows enthusiasm or excitement.
The crowd cheered enthusiastically as the band took the stage.
In a way that is aggressive or intense.
The lion roared fiercely to protect its territory from intruders.
In a way that is strong, resolute, or unwavering.
She stood firmly by her decision despite the criticism from others.
In a gentle and careful way.
She stroked the cat gently to avoid startling it.
In a smooth, controlled, and attractive way.
The ballerina moved gracefully across the stage.
In a happy or joyful manner.
She smiled happily when she saw her friend.
In a hurried or rushed manner.
He ate his breakfast hastily before rushing out the door.
In a truthful and sincere manner.
She spoke honestly about her feelings.
In a way that shows a strong desire or need for food.
He looked hungrily at the pizza on the table.
With strong feelings or emotions.
She stared intensely at the painting, trying to understand its meaning.
In a joyful or happy manner.
The children ran joyfully through the park.
In a kind or friendly manner.
She spoke kindly to the stranger and offered to help.
In a loud or noisy manner.
He shouted loudly to get his friend’s attention.
In a loving or affectionate manner.
She hugged her daughter lovingly when she arrived home from school.
In a crazy or wild manner.
He drove his car madly down the street, swerving and honking the horn.
In a mechanical or automatic manner, without emotion or attention.
After 20 years, we mechanically say ’I love you’ without feeling the emotion behind the words.
In a nervous or anxious manner.
She tapped her foot nervously while waiting for the job interview to start.
In a patient or tolerant manner, without getting angry or upset.
She waited patiently for her turn in line.
In a courteous and respectful way.
He politely declined the offer and thanked them for their consideration.
In a forceful and effective way.
The athlete swung the bat powerfully and hit the ball out of the park.
In a fast or speedy way.
She quickly finished her homework and went outside to play.
In a calm and soft way that makes little or no noise.
She quietly closed the door to avoid waking up the baby.
In a fast and quick way, often beyond control or comprehension.
The car rapidly accelerated down the road, leaving a trail of dust behind.
In a consistent and routine manner.
She regularly exercised every morning to maintain her health.
In a hesitant or unwilling way.
He reluctantly agreed to go to the party, even though he didn’t feel like it.
In a harsh or forceful manner, often without care or gentleness; violently. Approximately.
She roughly sketched the design on the paper.
In an impolite and disrespectful way.
He rudely interrupted the speaker and started talking about his own ideas.
In a way that does not cause harm or danger.
He safely stored the documents in a fireproof box.
In a way that is done or kept hidden from others.
The couple secretly planned a surprise party for their friend’s birthday.
1. In a sincere and solemn manner. 2. Severely.
She was seriously injured in the accident and had to stay in the hospital for several weeks.
In a sudden and quick manner, often with a cutting or critical tone.
The boss sharply criticised the employee for not meeting the deadline.
In a way that is quiet and without sound.
The cat silently stalked its prey, waiting for the right moment to pounce.
In a slow or leisurely manner.
She walked slowly through the park.
Without difficulty.
The car runs smoothly after the mechanic fixed the engine.
In a gentle or quiet manner.
She spoke softly to avoid waking up the baby.
In a serious or formal manner.
The judge solemnly declared the court in session.
Continuing or developing gradually or without interruption, at an unvarying pace.
Food prices have again risen steadily.
In a forceful or powerful manner.
She expressed her opinion strongly during the meeting.
In a sweet or kind manner.
She smiled sweetly at her little sister.
In a nervous or anxious manner.
He waited tensely for the interview results.
In a firm or secure manner.
She held onto the railing tightly to avoid slipping on the icy steps.
In a forceful or aggressive manner.
The storm raged violently throughout the night.
In a friendly or affectionate manner.
She greeted her old friend warmly when they met.
In a tired or exhausted manner.
He walked wearily into the house after a long day at work.
In a willing or enthusiastic manner.
She volunteered to help out willingly when asked.
In an enthusiastic or passionate manner.
He read every book zealously he could find on the subject.
5.4 Place
Most of the following adverbs can also function as prepositions.
At a higher place or position.
The evening was beautiful. The stars shone brightly above.
In or to a foreign country.
She went abroad to study for a year.
From one side to the other side of something.
The teacher walked across to greet the new student standing by the classroom door.
In front of or further forward than something else.
He took a step ahead to get a better view of the stage.
Running or extending in a specified direction, often beside something else.
The river flowed peacefully along, winding its way through the valley.
In a circle or in a surrounding area.
She looked around but couldn’t see anybody.
At a distance from a particular place or person.
“Don’t look away,” he instructed.
In or to a previous place or condition.
“Step back, there are land mines ahead of us,” said the officer.
At or to the far side of something, or in a position further back than something or someone else.
Don’t look behind, somebody is following us.
At a lower place or position.
I heard a loud noise coming from the apartment below.
In a lower position than something; under something.
She was laughing and making jokes with everyone at the party, but I could see that sadness was hidden beneath.
In or along the space separating two objects or regions.
I’ve made two appointments for today; I’ll try to grab lunch in between.
At or to the further side of something.
We could see the orchard and the wild meadows beyond.
At a short distance from something or someone.
Be careful! It’s a venomous snake. If you get too close, it might bite you.
On or to a lower floor of a building.
She went downstairs to get some water.
In or to all places.
There were flowers everywhere in the garden.
At, to, or by a great distance in space or time.
How far is it from here to the nearest beach?
In or at this place; where the speaker or writer is.
I’ve worked here for a long time.
At or to a point inside a space or container.
Could you call the children in for dinner, please?
Within the bounds or limits of something; in the interior.
Please come inside for dinner.
At or to a short distance from something or someone.
We were standing near enough to see the expression on his face.
At or to a short distance away; close at hand.
There is a coffee shop nearby.
At a distance from a particular place or point.
The thief ran off at high speed when they saw the police.
In a position touching and supported by a surface.
The bus driver started the engine as he was getting on.
Away from the inside or the center of something.
Today is not a good time to go out.
On or to the exterior of something or someone; away from the interior.
The children are playing outside.
Above.
A rainbow appeared over us after the rain stopped.
Beyond and done with; in the past.
The train left and we watched it go past.
In a circular direction or position; around.
I turned round and saw her crying.
To or from a side; sideways.
He fell sideways off the chair.
In, at, or to that place or position.
Put the books there.
In every part of; during the whole of.
The child painted the wall throughout.
Beneath the surface of the ground.
The underground cave is over 1000 years old.
In a higher position or place.
Let’s go up.
On or to a higher floor of a building.
The bedrooms are located upstairs.
Inside or enclosed by something.
I could hear a voice coming from within.
